Dental dilemmas in pregnancy
Curbside Consults delivers expert perspectives from physicians outside of the ob/gyn specialty to provide insight into various health issues affecting pregnant women, about which they are experts. This new section is the brainchild of Editorial Advisory Board member Christine Isaacs, MD.
Scenario 1: The Terrible Toothache
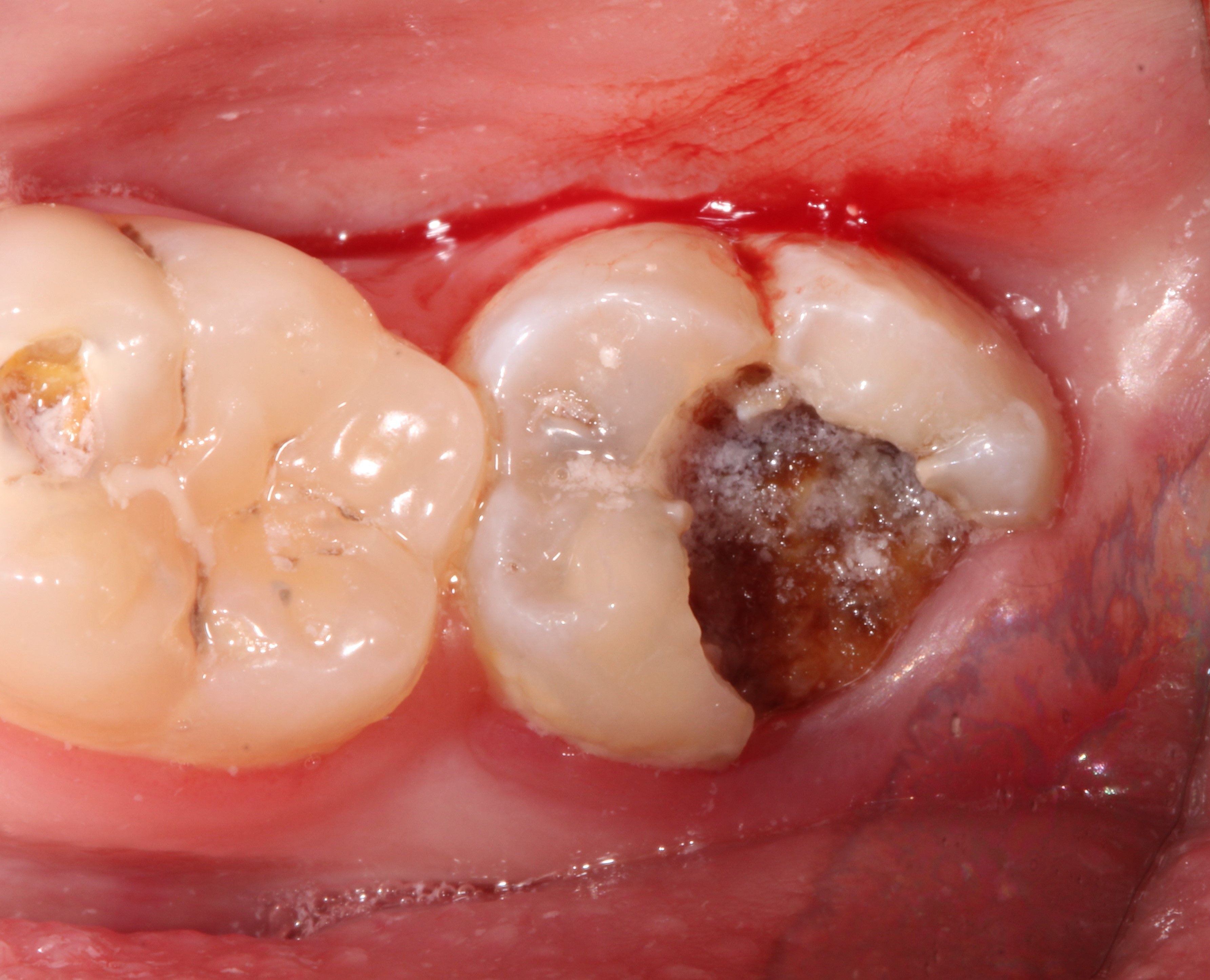
A 30-year-old patient presents to labor and delivery at 3 a.m. in tears. She is 32 weeks pregnant and complains of a “terrible toothache” refractory to acetaminophen and ice packs. She has no obstetric complaints. All vital signs and fetal surveillance are reassuring. You see the following (Figure 1):
Figure 1. Source: Virginia Commonwealth University Endodontics Clinic
What should you do?
In this scenario, the source of the pain is a cavity that has progressed to the innermost portion of the tooth (pulp) where nerves and blood vessels reside. Clinically, this is illustrated by the dark cavitation noted on the image. The pressure from the swelling can be excruciating and even involve the bone surrounding the tooth root. Definitive treatment likely requires extracting the tooth or cleaning the infection with a root canal if the tooth can be restored.
Initial management by an obstetrician can include:
- Comfort measures and referral to a dental provider for definitive treatment.
- Direct pain relief can be achieved with “dental balls” by prescribing lidocaine 2% mucous membrane solution to be mixed with equal parts of over-the-counter aluminum hydroxide/magnesium hydroxide and liquid diphenhydramine. Patients can be instructed to soak cotton balls in this mixture and apply them to the site of dental pain every 4 hours, as needed. The cotton balls should be refrigerated and discarded after 5 days.
2. Antibiotics may be considered when the patient has facial swelling.
3. To avoid any delay in dental treatment, proactively provide a medical clearance form stating that dental procedures with lidocaine with epinephrine are permissible.
Scenario 2: Puffy, Bleeding Gums
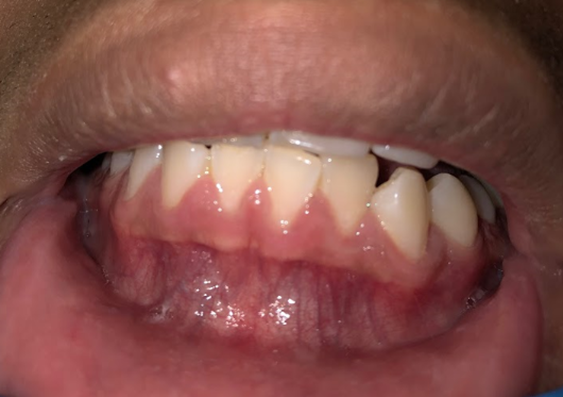
A 19-year-old patient presents for her routine prenatal care appointment at 14 weeks gestation and mentions her gums feel puffy, tender and swollen. Her gums bleed more frequently, and her exam appears in the image (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Source: Dental Department, Northwell Health
What should you do?
Patients who are pregnant can be at risk for the gum disease gingivitis, as illustrated in Figure 2. It’s theorized that changes in hormones can result in an exaggerated inflammatory response to bacteria, and thus, the inflamed gingiva.
Clinicians should stress the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing twice a day and seeing a dentist for routine care. Establishing a dental home early in pregnancy can help reduce the risk of dental emergencies in the future.
Scenario 3: Sensitive Teeth
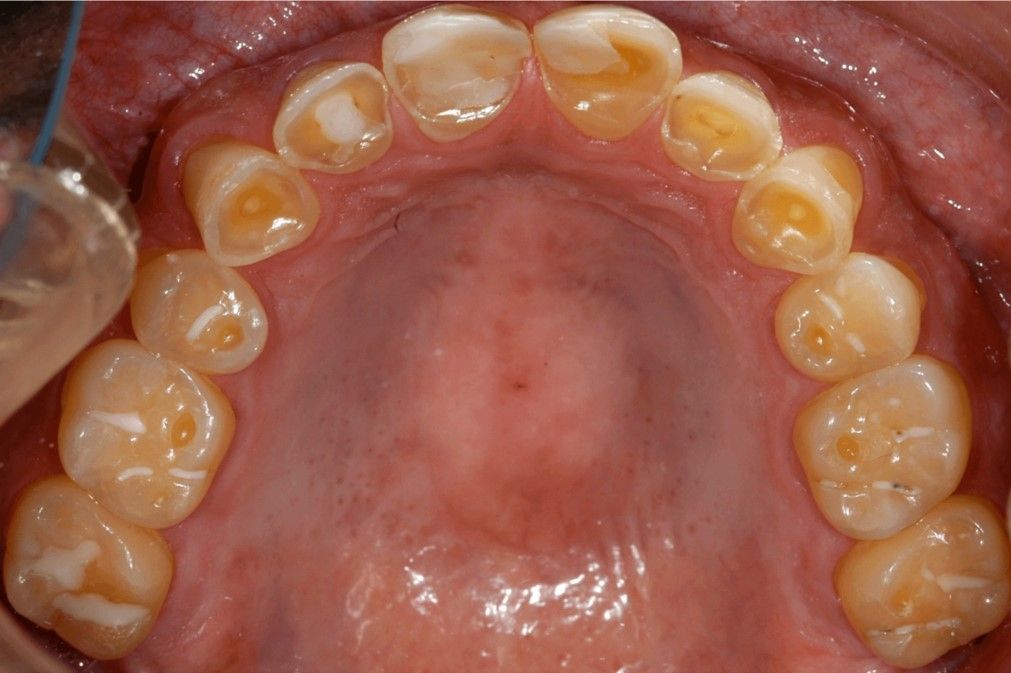
Your 35-year-old patient with hyperemesis gravidarum complains that her teeth are becoming more sensitive. You note the following on her exam. (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Source: Virginia Commonwealth University Oral Pathology Teaching Files
What should you do?
Acid from gastric secretions can cause erosions of the outermost layer of tooth structure (enamel) and expose the sensitive underlying yellow tooth structure (dentin), as illustrated in Figure 3.
The mouth relies on a healthy pH balance, so you can recommend a baking soda rinse for use after an emesis episode to help neutralize the acid. This is made by combining 8 oz. of water with 1 tsp. of baking soda to rinse in the oral cavity.
Although counterintuitive, patients should be instructed to wait least 1 hour after vomiting to brush their teeth and avoid gritty/abrasive toothpastes so as to not further erode the tooth enamel.
Scenario 4: A New Growth
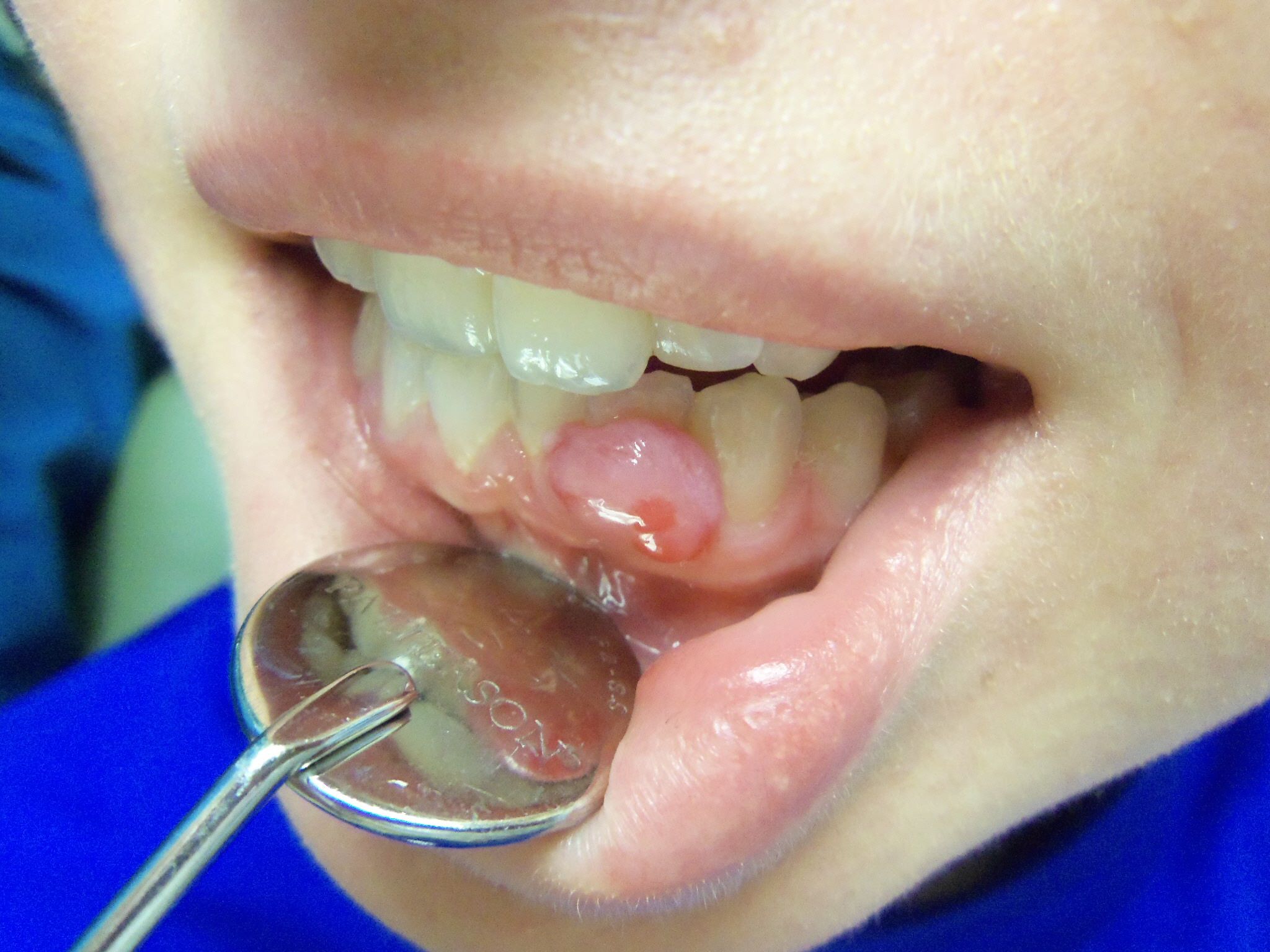
A 28-year-old patient in her second trimester is concerned about a rapidly growing red bump in her mouth. You note the following lesion on her gums (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Source: Virginia Commonwealth University Oral Pathology Teaching Files
What should you do?
This patient has a pyogenic granuloma, a finding so infamously associated with pregnancy that some call it the “pregnancy tumor.” This lesion is not a true granuloma or a tumor but rather a tumor-like growth associated with an exuberant response to local irritation of the gums (gingiva).
It can appear worrisome clinically due to its rapid growth and propensity to bleed. Because pyogenic granuloma has a high recurrence rate during pregnancy, dental providers will often defer treatment with surgical removal until after delivery, unless there are functional or aesthetic concerns at the time of diagnosis.
Additional resources

Severe maternal morbidity linked to mental health risks post-delivery
April 26th 2024A recent study revealed that severe maternal morbidity during pregnancy increases the likelihood of mental health hospitalizations or emergency department visits up to 13 years post-delivery, emphasizing the need for mental health screening.
Read More
S4E1: New RNA platform can predict pregnancy complications
February 11th 2022In this episode of Pap Talk, Contemporary OB/GYN® sat down with Maneesh Jain, CEO of Mirvie, and Michal Elovitz, MD, chief medical advisor at Mirvie, a new RNA platform that is able to predict pregnancy complications by revealing the biology of each pregnancy. They discussed recently published data regarding the platform's ability to predict preeclampsia and preterm birth.
Listen
Study finds antihypertensive treatment reduces uterine fibroids risk
April 23rd 2024A recent study revealed that patients with untreated or new-onset hypertension face elevated chances of uterine fibroid diagnosis, underscoring the potential of antihypertensive therapy in mitigating this risk among midlife individuals.
Read More
Unraveling preeclampsia: Insights into heterogeneity and intravascular inflammation
April 22nd 2024A recent study delved into the intricate clusters of term preeclampsia, shedding light on its diverse manifestations and the pivotal role of intravascular inflammation, paving the way for improved classification and management strategies.
Read More
