
New research reveals that women face worse heart attack outcomes than men, particularly when treated with beta-blockers, highlighting the need for sex-specific care.

New research reveals that women face worse heart attack outcomes than men, particularly when treated with beta-blockers, highlighting the need for sex-specific care.

A new study reveals hybrid closed-loop technology significantly improves glucose control for pregnant women with T1D.

Analysis of over 3100 patients shows women receive less intensive lipid-lowering therapy and are less likely to reach LDL-C targets compared to men, 5 years after acute coronary syndrome.
USPSTF now advises biennial breast cancer screening from age 40 to 74 years based on an evolving evidence base.

Nieca Goldberg, MD, discusses important news and updates in cardiovascular health among women from the early portions of 2024.

A recent study found breast arterial calcification on mammograms could help predict higher risk of stroke, cardiovascular death, and heart disease in women.

New research from ISC 2024 reveals an increase in stroke risk for Black women with treatment-resistant hypertension before age 35, underscoring critical disparities in healthcare.

Highlights from the HFSA 2023 annual scientific meeting discussing heart health in women.

An analysis of 7 international, longitudinal studies with nearly 20,000 patients details apparent increases in risk associated with daily alcohol consumption among healthy adults.

A study from Denmark leveraging more than 40 million years of follow-up data from patients dating back to the 1950s offers insight into the apparent increase in the risk of myocardial infarction associated with pregnancy loss in women and whether this same effect is observed in male partners.
An analysis of patient data from the greater Houston area suggests women were less likely to be routed to a comprehensive stroke center than their male counterparts, despite a greater symptom severity and comparable distance to the centers.
An ENDO 2023 analysis of data suggests women with PCOS were at a 47% greater risk of mortality relative to their counterparts without the common endocrine disorder.

A pair of studies presented at EULAR 2023 offer perspective on the potential for postpartum depression as well as symptoms of depression and anxiety during pregnancy among women with rheumatic disease.

An analysis of data from 3 European countries provides insight into the apparent increase in risk of atrial fibrillation associated with preterm births as well as LGA or SGA births.

A genome-wide genetic association study using mendelian randomization provides insight into the causal relationships between HDPs and coronary artery disease and ischemic stroke later in life.

An analysis of the HAPO Follow-up Study is shedding light on associations between birth weight categories and risk of diabetes 10-14 years after delivery in mothers.

Further adding to the discussion surrounding the impact of endocrine-disrupting chemicals, an analysis of data from the SWAN Multipollutant Study suggests increased exposure to phthlates was linked to a 30-63% increase in risk of developing diabetes among White women in midlife.
An analysis of data from the China Kadoorie Biobank study suggests cumulative exposure to estrogen was associated with stroke risk in postmenopausal women.

An analysis of registry data recorded in Denmark over a 4-decade period offers an overview of the risk of acute myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke incurred as a result of preeclampsia during pregnancy and how this risk changes over time.

In what investigators are calling the largest study of its kind ever conducted in the US, results of the 2-year study, which included more than 300 transgender or nonbinary youth, underline the positive benefits seen with receipt of gender-affirming hormone therapy among this patient population.

An analysis of data from a Cleveland Clinic database indicates calcium supplementation in older adults with aortic stenosis was linked to an increased risk of mortality and worsening aortic stenosis.

New research suggests pregnancies conceived with assisted reproductive technology were associated with a more than doubling in risk for acute kidney injury.

A cross-sectional study of more than 70k women suggests those with long or irregular menstrual cycles were at a 22% greater risk of NAFLD.

Data from an analysis of a SWAN substudy suggests increased exposure to PFAS was linked to an increased risk of incident diabetes during midlife among women.
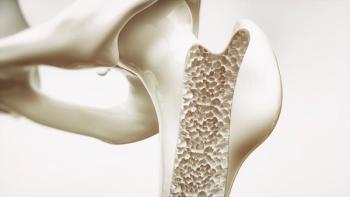
New research from the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) suggests assessments of anti-Mullerian hormone levels could help clinicians predict or detect bone loss among premenopausal women.

An analysis of data from more than 100k pregnant women suggests a history of spontaneous abortion was associated with an 18% increase in risk of subsequent gestational diabetes, with a history of multiple spontaneous abortions associated with an even greater risk.

A recent analysis suggests transfeminine individuals were at a 40% greater risk of developing diabetes than their cisgender counterparts, but this increase in risk was not attributable to gender-affirming hormone therapy.

Analysis of data from 83k matched pairs suggests statin initiation could increase a patient's odds of diabetes progression, including need for new glucose-lowering medications and new insulin use.
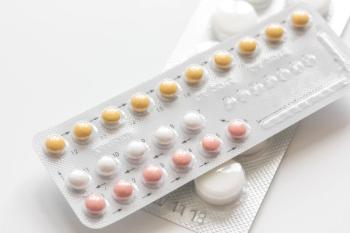
A pair of studies provide insight into the increased risk of dysglycemia among women with PCOS and the potential influence of combined oral contraceptive pills on this risk in a population-based cohort.

In an analysis of SWAN data, investigators found changes in menstrual cycle length within the 5 years preceding a woman's final menstrual period was associated with changes in carotid intima-media thickness and brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity.
Published: May 9th 2022 | Updated:

Published: August 31st 2025 | Updated: