
A retrospective study finds comparable pregnancy rates between PPOS and GnRH antagonist protocols, with a trend toward improved blastocyst outcomes in PPOS cycles.

A retrospective study finds comparable pregnancy rates between PPOS and GnRH antagonist protocols, with a trend toward improved blastocyst outcomes in PPOS cycles.

A new study shows extrauterine cerebellar ultrasound is a reliable, low-cost method to assess gestational age after fetal or neonatal death, especially in low-resource settings.

Vaccinating pregnant women at least 5 weeks before delivery significantly improves transplacental transfer of respiratory syncytial virus antibodies, offering better early protection for infants.

Childhood adversity may raise endometriosis risk, with exposure to violence linked to a twofold increase, a Swedish study finds.

A recent study presented at ACOG 2025 highlights the potential of once-weekly secnidazole oral granules as an effective long-term therapy for recurrent bacterial vaginosis.
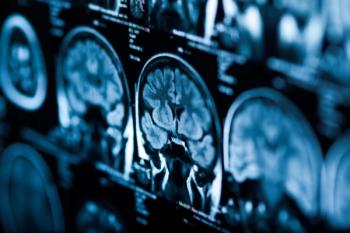
New research reveals that women with eclampsia show significantly higher rates of brain abnormalities, offering insight into unexplained neurologic symptoms during pregnancy.

Daily trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole in pregnancy reduced preterm births, especially in women with HIV, but did not significantly affect birth weight.

As strains of antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea spread, zoliflodacin provides an alternative oral treatment with non-inferiority to other methods.

Patients with non-English language preference face significant delays in definitive breast cancer surgery, according to new research.

Review some of the top stories from the Contemporary OB/GYN website over the last week, and catch up on anything you may have missed.
A new study reveals higher rates of severe maternal complications among Black and Hispanic patients with prior cesarean births, highlighting the need for equity-focused care strategies.

New research reveals women with polycystic ovary syndrome are more likely to experience infertility and give birth at an older age compared to women without the condition.

A new randomized trial shows Er:YAG laser therapy offers no significant benefit over sham treatment for managing female stress urinary incontinence at 6 months.

New 14-gene test allows early, precise assessment without partner samples.

A universal aspirin initiative at a Bronx hospital increased prescribing rates from 30% to 99% and is now being evaluated for its impact on preeclampsia.

New research highlights that women giving birth at age 30 years or older face significantly increased odds of pelvic organ prolapse.
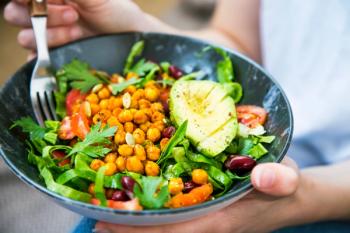
A low-fat, soy-rich vegan diet significantly decreases severe hot flashes and supports healthy weight loss, according to new research.

A phase 3 trial shows elinzanetant effectively reduces hot flashes and improves quality of life in patients undergoing hormone therapy for hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer.

Considerations for reducing blood loss, morbidity, and surgical complexity in patients with large fibroids.

A new study reveals that emotional symptoms such as anger and feeling out of control intensify before menstruation and become more severe during the menopause transition.

Integrating oral health checks into standard clinical assessments can improve overall patient outcomes and reduce the risk of systemic diseases linked to gum and dental issues.

New research reveals a strong genetic connection in postpartum psychosis, emphasizing the need for early screening in high-risk women.

Take a quick look at everything you may have missed last month, including the latest FDA updates, top stories, and exclusive interviews.

New research reveals a strong connection between poor oral health, oral microbiota, and heightened pain sensitivity in women with central sensitisation disorders.

Review some of the top stories from the Contemporary OB/GYN website over the last week, and catch up on anything you may have missed.
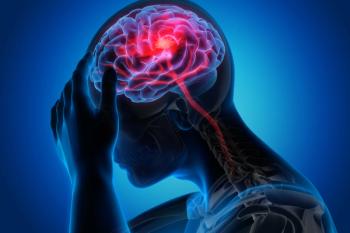
A new study reveals that combined oral contraceptive use significantly increases the risk of cryptogenic stroke in women aged 18 to 49 years, highlighting the need for careful risk assessment.

Women with dense breast tissue face higher cancer risks and diagnostic challenges, but new research reveals contrast imaging may significantly improve early detection.

A new study reveals worsening mental and physical health among female parents, highlighting growing disparities across race, income, and family structure.

A new University of British Columbia study reveals that mild breast symptoms before menstruation are more common in cycles with normal ovulation than in disturbed ones.

GSK and Spero Therapeutics announced that the phase 3 PIVOT-PO trial for tebipenem HBr, a potential first oral carbapenem for cUTIs in the United States, was stopped early because of positive efficacy results.