Discover how recent research unveils platelet-rich plasma as a promising alternative treatment for various pelvic floor disorders, offering hope for improved quality of life for affected individuals.

Discover how recent research unveils platelet-rich plasma as a promising alternative treatment for various pelvic floor disorders, offering hope for improved quality of life for affected individuals.

A recent systematic review highlighted a half-dozen methods to improve antenatal STI screening in low- and middle-income countries in need of better options.
A recent study revealed the efficacy of tetrazole oteseconazole against fluconazole-resistant Candida biofilms, offering hope for recurrent candidiasis patients seeking alternative therapies.

Recent study reveals the need for customizable electronic partner notification platforms for gonorrhea and chlamydia, highlighting the need for tailored solutions to improve sexually transmitted infection partner services.

A randomized trial among young Kenya women showed the post-exposure prophylactic was insignificantly more effective in preventing chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis—largely due to inadherence.

Discover how metabolomics sheds light on potential biomarkers for early detection and treatment of Candida albicans-induced vulvovaginal candidiasis, offering crucial insights into the pathogenesis of this prevalent inflammatory condition.

Discover how low folic acid levels during pregnancy heighten the risk of adverse outcomes including miscarriage and preterm delivery.

A recent investigation finds comparable safety and effectiveness between intravenous and intramuscular oxytocin administration, suggesting intramuscular administration may be preferable for postpartum hemorrhage prevention.

A recent investigation sheds light on patient preferences and concerns regarding external cephalic version versus cesarean section for managing fetal malpresentation, revealing gaps in counseling and the desire for more information.
Misunderstandings surrounding bacterial vaginosis can delay treatment, but advancements such as XACIATO offer effective solutions, emphasizing the importance of open communication and continued research for comprehensive women's health care.

Review some of the top stories from the Contemporary OB/GYN website over the last week, and catch up on anything you may have missed.

Enmetazobactam (Exblifep; Orchid Pharma) gains FDA approval for treating complicated urinary tract infections in adults after demonstrating superiority over piperacillin-tazobactam in clinical cure and microbiological eradication in a global phase 3 trial.

A recent investigation sheds light on the efficacy of hormone therapy in alleviating depressive symptoms associated with menopause, revealing potential benefits for women undergoing natural menopause.

The FDA has issued a Complete Response Letter for the New Drug Application of cefepime-taniborbactam, requesting additional chemistry, manufacturing, and controls data.

Recent research suggests AI computer vision technology could bolster the accuracy of HIV self-testing, potentially advancing HIV service accessibility and acceptance to meet Sustainable Development Goals.

Recent research highlighted the significant correlation between adverse childhood experiences and heightened risks of preeclampsia and depression during pregnancy.

Following a landmark decision regarding the status of embryos, the University of Alabama at Birmingham has suspended in vitro fertilization services, sparking concerns over reproductive rights and health care access as experts grapple with the legal aftermath.
Recent research highlighted an association between the total dose of prescribed opioids during pregnancy and the heightened risk of spontaneous preterm birth, emphasizing the need for judicious opioid use in pain management for expectant mothers.
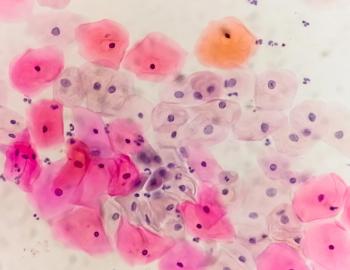
A recent study evaluated the safety and effectiveness of the Onclarity HPV assay in detecting high-grade cervical disease, presenting findings on its comparability to predicate assays and potential for cost-saving benefits in screening practices.
Discover how immediate postoperative symptom burden varies between open and minimally invasive hysterectomies under enhanced recovery after surgery protocols, shedding light on recovery disparities in gynecologic surgery.

A recent study revealed that physical activity confers greater reductions in all-cause and cardiovascular mortality risk among women compared to men, emphasizing the importance of closing the gender gap in exercise participation.


Discover key findings from a comprehensive study on in vitro fertilization outcomes among women with obesity, shedding light on the importance of equitable access to fertility treatment regardless of body mass index.

New meta-analysis reveals heightened risks of major congenital malformations and respiratory distress syndrome in infants born to mothers with asthma, underlining the importance of proactive management during pregnancy.

Recent research highlights the efficacy and safety of relugolix combination therapy in managing uterine fibroid-associated heavy menstrual bleeding specifically among Black women, demonstrating outcomes comparable to the broader population.

Review some of the top stories from the Contemporary OB/GYN website over the last week, and catch up on anything you may have missed.

New research from ISC 2024 reveals an increase in stroke risk for Black women with treatment-resistant hypertension before age 35, underscoring critical disparities in healthcare.


The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's latest report unveils a 222% rise in maternal syphilis cases per 100,000 live births from 2016 to 2022, with increases observed across racial, age, and perinatal care groups nationwide.