
To properly measure risk, the author argues, researchers must compare 1 twin pregnancy with 2 consecutive singleton pregnancies.

To properly measure risk, the author argues, researchers must compare 1 twin pregnancy with 2 consecutive singleton pregnancies.

The percentage of married women aged 15–44 who were infertile fell from 8.5% in 1982 (2.4 million women) to 6.0% (1.5 million) in 2006–2010, according to a new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).

Mobile healthcare apps and devices are expected to grow at a rate of 61% a year, with 50% of healthcare professionals using at least one app. Ob/gyns are leading the charge, and these 8 apps are helping MDs and HCPs manage patients and stay current on everything happening in the field.

There is no evidence that intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection (IMSI) provides subfertile patients an additional benefit over the standard intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).

Depression over an extended period may make it more difficult for women to get pregnant.

Bisphenol-A (BPA) has been making headlines for potential connections with neurologic conditions, obesity, and myriad other health concerns. A recent study published in Human Reproduction looked at whether BPA had a negative impact on fertility.

Implantation rates in unstimulated IVF cycles compared favorably with those in stimulated IVF cycles in a retrospective analysis.

While one expert feels that the benefits for family balance outweigh potential risks, the other is concerned that sex selection will lead to a slippery slope.

In vitro fertilization (IVF) is associated with an increased risk of venous thromboembolism and pulmonary embolism, especially during the first trimester.

Results of a study of more than 116,000 women, published online May 14 in Human Reproduction reveal a 39% lower risk of endometriosis in those who were morbidly obese than in women with normal body mass index (BMI).

There is insufficient evidence to determine that hormonal contraceptives do not influence glucose and lipid metabolism in women with diabetes mellitus, concluded a systematic review conducted by the Cochrane Fertility Regulation Group.

"Should all women freeze their eggs?" This question was posed by Marcelle Cedars, MD, during a Tuesday afternoon session at ACOG's 61st annual clinical meeting. In a session offering late-breaking news from SGO, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM), the American Urogynecologic Society (AUGS), and the Society for Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility (SREI), Dr. Cedars pointed out that as of October 2012, ASRM no longer considers egg freezing experimental.

The Contraceptive CHOICE Project, a research study at Washington University in St. Louis, found that offering long-acting, reversible contraception (LARC) to women first, citing its low-failure rates, reduced rates of unintended pregnancy and abortion and increased continuation rates.

Uterine artery embolization for fibroids results in a tremendous reduction in menorrhagia. But while complication rates are low, up to 15% of patients are readmitted for indications like pain, bleeding and infection.

In October 2012, the American Society of Reproductive Medicine announced it no longer considers oocyte freezing experimental. This raises complex questions about how to counsel patients who wish to preserve eggs for social indications.
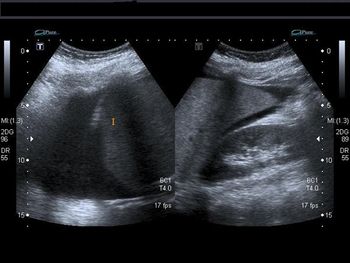
This young lady has abdominal pain and chest discomfort.She was undergoing treatment for infertility.What is your diagnosis?

In patients with an American Fertility Society class V or class VI septate uterus, hysteroscopic metroplasty is associated with a significant improvement in reproductive performance.

This patient presented with 18 months of secondary infertility following a second trimester dilation and extraction.

The use of a postoperative levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device reduces the recurrence of painful periods in women with endometriosis.

Women with endometriosis who undergo surgery to treat the condition are less likely to have ovarian cancer develop later in life.

Recombinant pigment epithelium-derived factor (rPEDF) proposed as a novel physiological treatment for ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).

For the long protocol of down regulation in in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycles, are depot and daily gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (GnRHa) equally effective?

Hysteroscopic removal of polyps in women with unexplained infertility may increase their chances of becoming pregnant, concludes an intervention review conducted by the Cochrane Menstrual Disorders and Subfertility Group.

Immediate start of hormonal contraception may reduce unintended pregnancies and increase method continuation, but the evidence is limited, according to the findings of an intervention review conducted by the Cochrane Fertility Regulation Group.

A registry-based study by researchers at UC San Francisco (UCSF) has shown an association between BRCA1/2 mutations and early menopause. The findings, published in Cancer, suggest that women who carry the genetic defect may be at risk of earlier infertility.