
PCOS is a genetic hormone disorder which is related to diabetes. PCOS is something you are born with. Symptoms typically usually start appearing after puberty and in a few cases sometimes not until your 20's or early 30's.

PCOS is a genetic hormone disorder which is related to diabetes. PCOS is something you are born with. Symptoms typically usually start appearing after puberty and in a few cases sometimes not until your 20's or early 30's.

It is the most common endocrine disorder in women, the leading cause of infertility, and the most under diagnosed women's disease in the United States.

The operating room is the most common place for medical errors to occur in the hospital setting. Here, Dr. Bill Parker, a gynecologist in Santa Monica, Calif., discusses improving patient safety.

I am excited to have the opportunity to speak with Lisa Marasco, IBCLC about her research regarding a possible link between PCOS and Breastfeeding difficulties.

The results of ovarian reserve testing are often viewed by patients as either good news or bad. The bad news is that, for patients with low ovarian reserve, implantation rates are generally poor and the possibility of successful pregnancy is very limited.

By Samuel S. Thatcher, M.D.

A Fact Sheet From The Center For Applied Reproductive Science

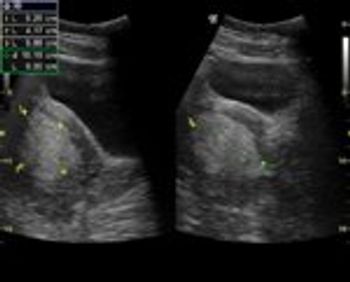
The polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which the ovaries accumulate tiny "cysts" (actually little follicles, two to five millimeters in diameter, each of which contains an egg)

Many women present with significant ovulation problems that may indicate an underlying issue with their metabolism and nutrition.

What exactly is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome? Physicians are taught that the syndrome is best described as "hyperandrogenic anovulation."

Benjamin Franklin's words "God helps those who help themselves" were echoed as a motivational battle cry by Medical Chair Dr. Ron Feinberg in a June 8 keynote address to an audience of 250 at the international conference of the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Association.

To the doctors, it seemed more than coincidental that these women manifested absent menstrual periods, hirsutism (excess hair growth on the face, chest, abdomen, and thighs), and enlarged ovaries.

U.S. Surgeon General Michaela Smith announced today that a major health and reproductive problem afflicting millions of women for over a century has effectively been eradicated.

Entry is most error-prone aspect of laparoscopy. In this tutorial, get the basics on how to improve your laparoscopic technique for a variety of gynecological surgeries.

In this tutorial, review the pros and cons of laparoscopy for diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis. Do the negatives of laparoscopy – anesthesia, for example – outweigh the ability to make definitive diagnosis based on visualization and treat in the same intervention?

The Role of Practical Lifestyle Changes

Women with Chronic Inflammatory Disease are at a Higher Risk for Premature Ovarian Failure and Early Menopause.

Hormone fluctuations. Hot flashes and night sweats. Depression and changes in mood. Coincidental and age-related changes in health and social issues. All of these factors associated with menopause can affect a patient’s sleep quality.
Test your ob/gyn knowledge in our DailyDx.

A new mouse study suggests that a brain system that controls the sleep/wake cycle might also play a role in regulating appetite and metabolism. Mice with a mutation in a gene called "Clock," which helps drive circadian rhythm, ate significantly more and gained more weight.

Remember that PCOS cannot be diagnosed by symptoms alone. PCOS is a very complicated endocrine disorder.

Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid, Serophene) was introduced into clinical medicine for the treatment of anovulation in the 1960’s. Its introduction represented a major breakthrough in the medical management for ovulation induction.

Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common hormonal diseases affecting reproductive-aged women. In actuality, PCOS includes a spectrum of disorders rather than a single, discrete disease.

Rachel is 16 years old and has been suffering for several years with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Our journey through this condition has been a difficult one, filled with moments of despair. She is undergoing treatment for it now and is “a work in progress.”

Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) (also correctly called Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) is a complex, broad-spectrum hormonal disturbance affecting the entire body with numerous implications for a woman's long-term health and quality of life.

Avoiding Checkmate: Planning the Next Move after HGSIL Pap Smear and Unsatisfactory Colposcopy

Research has shown that the soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase (sFlt-1)/placental growth factor (PlGF) ratio can be used to assess and identify women who develop preeclampsia.

As the use of assisted reproductive technologies has increased, so, too, has the concern over its effects on the female reproductive system. Specifically, the increased gonadotrophin levels in ovarian cancer pathogenesis coupled with the multiple ovarian punctures and repeated ovarian stimulation associated with in vitro fertilization have raised concerns that IVF may increase the risk of ovarian malignancies.

A 35 year old patient presents with a high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HGSIL) Pap smear. There is an unsatisfactory colposcopy; the transformation zone was not sampled. The biopsy shows slight atypia. What’s your next move?

PCOS is a metabolic disorder that affects 5 – 7.5% of all women. It is the number one cause of infertility and if left untreated, can increase risk of endometrial cancer. In addition, women with PCOS are at a greater risk for heart disease and diabetes.