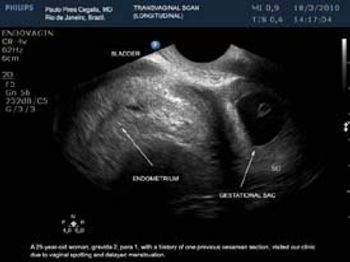
This is a confirmed case of scar ectopic pregnancy. Yesterday, I carried out this exam in an emergency room, without much time to perform an adequate sonogram, the patient did not feel good with “cramps” but no signs of bleeding.

This is a confirmed case of scar ectopic pregnancy. Yesterday, I carried out this exam in an emergency room, without much time to perform an adequate sonogram, the patient did not feel good with “cramps” but no signs of bleeding.
Normal aspect of the ossification centers of the fetal sternum at 33 weeks. Size of the ossification centers decreases in a cranio-caudal sense.
Leiomyoma that has undergone fatty degeneration.
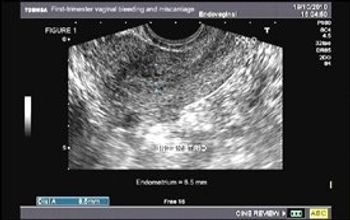
Sagittal image from a transvaginal sonogram in a patient with bleeding after a spontaneous abortion. The endometrium (between cursors) was thick and heterogeneous, measuring 8.5 mm in thickness (Fig1). Color doppler image in same patient shows focal flow (Fig. 2 - arrow) within the heterogeneous endometrium.
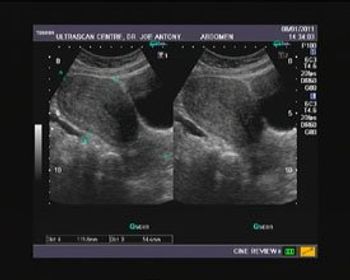
Images of "Bulky Uterus"
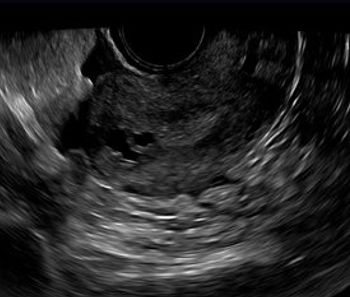
Cystic spaces in the sub-endometrial myometrium of the fundus.
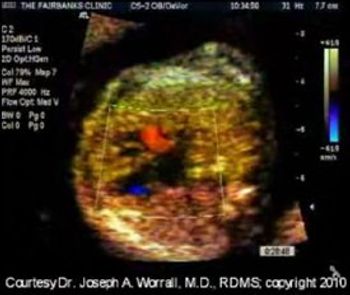
The patient was a 38 year old G4 P3, 20w4d. I was doing an anatomic survey today. While I was looking at a long axis view of the fetal heart with color Doppler, the baby developed hiccups, and with each contraction of the fetal thorax (which was quite obvious) I could see an explosion of blue color representing blood going through the foramen ovale from right to left.

Although ultrasounds are relatively safe and have become integral tools in medicine, the underlying thermal and mechanical mechanisms have the potential for causing negative biological effects. To protect patients, the National Electrical Manufacturers Association developed standards requiring the on-screen display of thermal indexes (TI) and mechanical indexes (MI) on machines capable of producing MIs or TIs greater than 1.

One in nine women will develop breast cancer during her lifetime, provided she lives to age 85. Most breast cancer is NOT genetically linked – less than 16%. In the study by Stavros et al., July 1995, – over 80% of all sonographic, biopsy proven, solid nodules were benign.

At the time I was starting this blog two patients with similar fibroids came to see me. Both were severely anemic, and one was hemorrhaging and in shock.

Doppler ultrasonography (US) is increasingly being utilized as an imaging modality in breast cancer. It is used to study the vascular characteristics of the tumor.

This random retrospective cross-sectional study was preformed to determine the frequency of uterine malformation in restricted gene pool communities. In 4 groups of women desiring to conceive during their reproductive years, all women lives in lacrete, a community in north Alberta, Canada

Three-dimensional ultrasound (3D US) is a new imaging modality, which is being introduced into clinical practice. Although this technique will not probably replace two-dimensional ultrasound, it is being increasingly used.
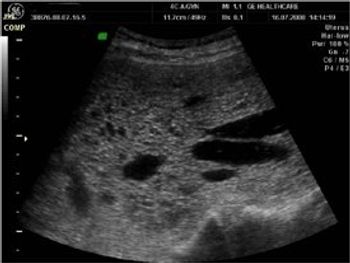
Complete Invasive Mole
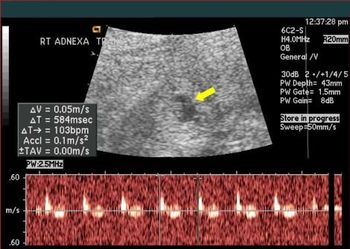
A 29-year-old gravida 10, para 3 (1 term gestation, 1 preterm gestation of twins, 1 stillbirth at 5 months, 2 spontaneous abortions, and 4 elective abortions) presented to the clinic at about 5 weeks’ gestation with abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. She described the pain as sporadic, mostly on the left side, exacerbated by movement, and resolving with rest, and the bleeding as initially intermittent but then heavier “like a period.”
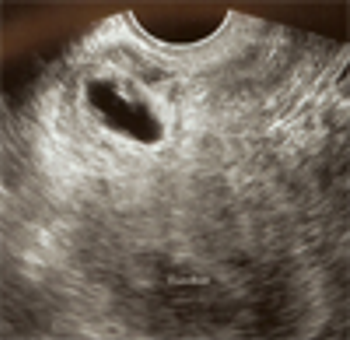
Implantation in the scar of a previous Cesarean is thought to be the rarest of ectopic pregnancies. With the increasing numbers of Cesareans performed, scar implantation may become more frequent as well. We present an illustrative case.
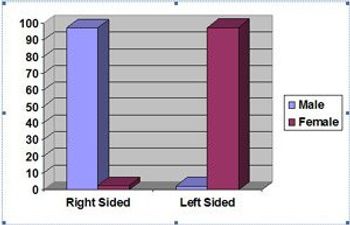
This study contributes to advances in knowledge by understanding the history of fetal gender and the ethical dilemma of choosing or detecting fetal gender at first trimester of the pregnancy. It gives new prospective and method to detect fetal gender as early as possible to better manage some genetic disease which can be found in male or female fetuses.

More than half of the 600,000 hysterectomies performed in the 1900s involved bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and it has been estimated that many of those were performed solely to reduce the risk for ovarian cancer. While there has been increased knowledge in the risk in women with familial history, a knowledge gap still exists for other women, which could lead them down the path of potentially unnecessary surgery

Clinicians and researchers have seen an increase in the prevalence of gastroschisis, with the greatest risk seen in women who are younger than 20 years. That, coupled with an evident increase in developing countries, has led researchers to believe that gastroschisis is associated with environmental factors (with or without underlying genetic susceptibility).

Persistent infection with HPV is the principal cause of cervical cancer, with HPV implicated in more than 99% of cervical cancer cases worldwide.1 The cobas HPV (human papillomavirus) Test, recently approved by the FDA, identifies women at highest risk for the development of cervical cancer.

Screening for osteoporosis should be conducted for all women 65 years and older and for younger women whose fracture risk is equal to or greater than that of a 65-year-old woman who has no additional risk factors, according to a US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommendation statement draft. The proposed new USPSTF guideline would broaden the 2002 version, which recommended routine screening only for women 65 years and older and women aged 60 to 64 years who are at increased risk for osteoporosis fractures.

Patients are using email to communicate with their doctors more than ever. But what are they corresponding about? A group of researchers recently evaluated unsolicited emails sent from patients to their general obstetrician-gynecologist to better understand why patients email their physicians.

There is no denying that we live in a fast-paced, communications-driven world. Email is increasingly being used for business and personal communications, but how has this impacted communications between patients and their doctors?
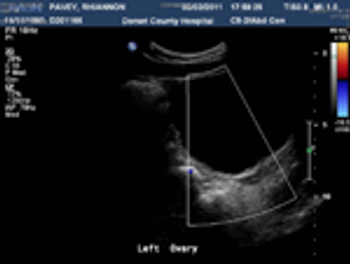
Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome affects at least 1 in 4500 female births.1 The syndrome consists of vaginal aplasia with other müllerian duct abnormalities. The characteristic feature of MRKH syndrome is congenital absence or underdevelopment of the upper vagina and uterus; it is rarely associated with unilateral renal agenesis, ectopia, or horseshoe kidney.

When it comes to consulting with their doctors, Americans are not averse to email but do not like the idea of using social media such as twitter or Facebook.

Evidence is mounting that pelvic organ prolapse results from a disruption in the balance between the buildup and breakdown of the extracellular matrix in pelvic tissues.

The American Medical Association introduced its first-ever "app," an on-the-go reference guide that helps physicians determine the appropriate current procedural terminology evaluation and management billing codes.

Working 11 hours per day instead of 7 to 8 may make you wealthier, but it also may be deadly.

Worried about financial pressure and the effects of healthcare reform, an increasing number of physicians are considering making changes in how they practice medicine.

Thyroid disorders are among the most common endocrinopathies encountered during pregnancy.