
Get caught up with Contemporary OB/GYN! This list helps you navigate our top stories from the week, all in one place.

Get caught up with Contemporary OB/GYN! This list helps you navigate our top stories from the week, all in one place.

Data supporting the safety of influenza, pertussis, and COVID-19 vaccines in pregnancy remain strong, even as policy shifts raise concerns about future HPV vaccination recommendations, Kevin Ault, MD said.

In a large preconception cohort, more than 40% of pregnancy planners reported very early home pregnancy testing, which was associated with higher risks of false-negative results and detection of very early pregnancy losses.

"It really is important for us to be able to explain to women the why. Why are we doing this?" said Barbara Levy, MD, in this Contemporary OB/GYN interview.

A Chinese study found that menstrual blood HPV testing had a comparable diagnostic accuracy to clinician-collected cervical samples in detecting CIN2+ and CIN3+.

Kevin Ault, MD, of the NFID, explains the importance of data- and evidence-based guidance, such as that of ACOG, for maternal immunization recommendations.

A new ACOG Committee Statement outlines how immigration status affects health outcomes and calls for enforcement-free health care settings.


ACOG continues to support maternal immunization against COVID-19, flu, and RSV amid growing public questions about vaccine safety during pregnancy.

Take a look back at any of our expert video interviews you may have missed from January 2026.

Take a quick look at everything you may have missed in January, from our latest video interviews to new clinical trial data to a FAQ on cervical cancer.

“We do know that women, their intention to breastfeed is a very strong predictor of them successfully breastfeeding. Those conversations in pregnancy are very important," said Fionnuala McAuliffe, MD, in this Contemporary OB/GYN interview.

Trial shows higher sensitivity with AI-supported breast cancer screening.

Federal guidance now designates primary hrHPV testing every 5 years as the preferred cervical cancer screening method for most average-risk women aged 30 to 65 years and adds patient self-collection as an acceptable option.

The scope of the marketplace contrasted sharply with the available evidence.

Winok Lapidaire, PhD, explains how early postpartum physician-guided blood pressure self-management after hypertensive pregnancy was associated with higher white matter volumes.

Universal prenatal syphilis screening legislation in Michigan was followed by substantial increases in early third-trimester testing among Medicaid enrollees.

United States labor induction rates have expanded to 37 and 38 weeks despite a lack of randomized evidence supporting non–medically indicated induction before 39 weeks.

The pause request comes as the administration considers whether to keep current federal rules in place that allow for remote access to mifepristone.

A central focus is understanding and reducing patient-level barriers to timely, values-congruent fibroid care

A new AHA scientific statement outlines how earlier prevention, rapid diagnosis and timely treatment can reduce the risks of maternal stroke during pregnancy and postpartum.

New national data show major declines in RA mortality among older women, alongside enduring racial and geographic inequities.

Menopause was associated with increased anxiety, depression, sleep problems and reductions in grey matter in key brain regions.

New FDA guidance and AACR-bound data highlight Aviva Bio’s progress in developing a differentiated testosterone therapy aimed at reducing breast cancer risk in women.
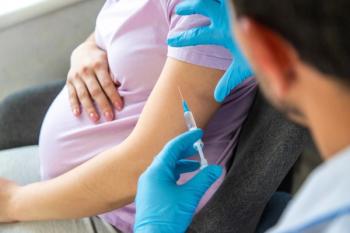
The AAP'S 2026 schedule has been endorsed by 12 medical and health organizations, including the American College of Nurse Midwives and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.

Get caught up with Contemporary OB/GYN! This list helps you navigate our top stories from the week, all in one place.

Longer lifetime breastfeeding was associated with lower odds of depression and anxiety up to 10 years later in a prospective cohort of midlife women.

In patients with diet-controlled gestational diabetes, continuing pregnancy beyond 39 weeks was associated with increasing maternal and neonatal risks.

A large cohort study found that prenatal exposure to acid-suppressive medications was not associated with neuropsychiatric disorders in children.

Self-collected hrHPV testing, now supported in HRSA’s cervical cancer screening guidelines, could dramatically expand screening according to Barbara Levy, MD.