Breast Health
Latest News
Latest Videos
Shorts
CME Content
More News
Experts release first clinical guidance on polygenic risk scores for breast cancer, outlining integration into screening and prevention strategies.
Wendie Berg, MD, PhD, explains new breast density reporting standards, cancer risks, and the importance of supplemental imaging for dense breast tissue.
In a recent study, older women receiving messages about breast cancer screening cessation were more likely to support stopping screening than those who did not receive a message.

A recent study found that hormone therapy use in breast cancer patients aged 65 years and older is associated with a reduced risk of Alzheimer's and related dementias.

A recent study from France demonstrates that incorporating hepatitis C virus screening into breast cancer programs significantly improves patient engagement and access to effective antiviral treatments among older women.

A recent study reveals that non-Hispanic White women living in deprived neighborhoods face higher breast cancer mortality, highlighting the impact of social determinants on health outcomes.

A recent study found breast arterial calcification on mammograms could help predict higher risk of stroke, cardiovascular death, and heart disease in women.

This lecture, presented by Holly J. Pederson, MD, at The Menopause Society 2023 Annual Meeting, looked at combined oral contraceptives in BRCA carriers and other high-risk patients, and hormone therapy in postmenopausal gene carriers as well as other high-risk women.

Multiple hormonal and non-hormonal therapies are available for treating genitourinary syndrome of menopause in breast cancer survivors, but combination therapies are the most effective.

In a recent study, women diagnosed with cancer during pregnancy and postpartum periods experienced greater rates of mortality than those diagnosed outside of pregnancy.

In a recent study, ChatGPT provided accurate and consistent answers to 22 out of 25 questions on breast cancer screening.

In a recent study, the risk of developing breast cancer was greater in women with current or recent use of progestogen-only contraceptives.

An analysis of data from more than 8400 postmenopausal women with a history of early-stage nonmetastatic, ER-positive breast cancer suggests there was no increase in risk of breast cancer recurrence or mortality observed with use of vaginal estrogen therapy or menopausal hormone therapy.
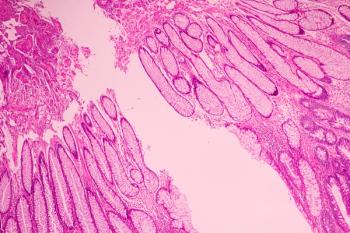
Steven J. Chmura, MD, PhD, discussed recent findings from the phase 2R/3 NRG-BR002 trial in patients with newly diagnosed oligometastatic breast cancer.

Gynecologists and physicians, in concert with mothers, are key not only to a woman’s early awareness of both breast cancer and mammography but to awareness of breast cancer risk factors as well.
Cancer programs seek to remove barriers to screenings.

Alexander B. Olawaiye, MD, discusses how social and biological determinants can affect care outcomes across cancer subtypes and what steps community and academic oncologists can take to ensure these disparities are recognized.
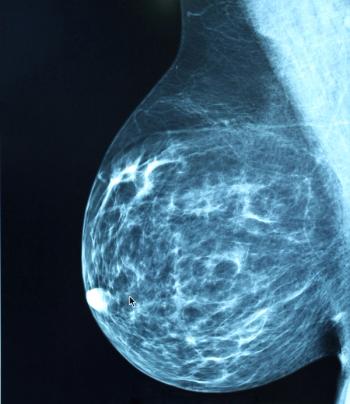
Novel therapies could potentially expand the population of patients with ERBB2-positive metastatic breast cancer who experience long-lasting disease response, according to a review in JAMA Oncology.
A quality improvement study in JAMA Network Open has found that a significantly lower percentage of patients with breast cancer presented with stage I disease before the COVID-19 pandemic, in 2019, compared to after the start of the pandemic, in 2020.
Trastuzumab deruxtecan resulted in a statistically significant improvement in progression-free survival and overall survival compared with physician’s choice of chemotherapy in patients with HER2-low unresectable and/or metastatic breast cancer, irrespective of hormone receptor status, meeting the primary and secondary end points of the phase 3 DESTINY-Breast 04 trial.

The campaign emphasizes the importance of annual cancer screenings with the Queen of Hip-Hop Soul
Investigators of the SWOG S1007 RxPONDER trial found a statistically significant improvement in invasive disease-free survival and distant relapse-free survival in premenopausal women who received adjuvant chemotherapy.
Compared with tamoxifen, aromatase inhibitors were revealed to be more effective in reducing the rate of recurrence in ER+ breast cancer among premenopausal women receiving ovarian suppression.

In using the biomarker approach to the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer, the challenge for the clinician is prioritizing the available treatment options based on the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines for breast cancer, which focus on active agents, preferred single-agent chemotherapy approaches, and doublet options for certain patients at high risk.

Certain post-menopausal women with HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer may be able to only undergo endocrine therapy after surgery – sparing themselves from the chemotherapy side effects.