Obstetrics
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Women with prior pre-eclampsia develop cardiovascular (CV) risk factors nearly a decade earlier, prompting calls for earlier and regular CV screening.

Discover key strategies OB-GYNs can use to protect pregnant women from severe COVID-19 risks and ensure healthier maternal outcomes.

New research reveals that both COVID-19 infection and broader pandemic-related stressors significantly impact pregnancy outcomes, including increased rates of preterm birth, low birth weight, and neonatal intensive care unit admissions.

Pregnancy may lower Long COVID risk, with researchers linking immune changes to reduced symptoms, though some groups remain vulnerable.

A new study highlights the benefits of doula care, showing increased vaginal birth after cesarean rates, reduced preterm births, and improved postpartum care among diverse patient populations.
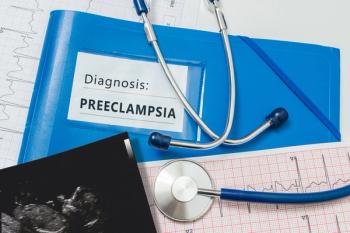
A new study reported how a soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 to placental growth factor ratio can help predict preeclampsia progression, aiding in risk assessment and optimizing patient care.

A recent study highlights the heightened risk of perinatal mortality in pregnancies affected by type 2 diabetes, emphasizing the need for improved prenatal care and risk management.

The 2025 Canadian Postpartum Guidelines recommend at least 120 minutes of weekly exercise, daily pelvic floor training, and improved sleep hygiene to enhance maternal and infant health.

A recent study identified key outcomes for vasa previa diagnosis and treatment, uniting patient experiences and clinical expertise to improve future research and guidelines.

A new study found that Black and American Indian birthing individuals in the United States are more likely to deliver at lower-quality hospitals than White patients, highlighting systemic health care inequities.

A recent study identified distinct gene signatures in placentae from gestational diabetes and pregestational diabetes pregnancies, offering potential for improved diagnosis and treatment strategies.

A study found that a first trimester circulating microparticle biomarker can help predict spontaneous preterm birth risk, potentially improving early intervention and neonatal outcomes.

A recent study suggests that the soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 to placental growth factor ratio can help predict clinical deterioration, intrapartum fetal distress, and mode of delivery, offering valuable insights for patient counseling and labor management.

Review some of the top stories from the Contemporary OB/GYN website over the last week, and catch up on anything you may have missed.

A recent study reveals significantly lower initiation and continuation rates of Mother’s own milk feeding among late preterm infants compared to other gestational age groups, highlighting a need for targeted support.

A recent study found that women with a history of gestational diabetes who sleep less or snore regularly face a significantly higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.

Review some of the top stories from the Contemporary OB/GYN website over the last week, and catch up on anything you may have missed.

A recent study reveals that Black, Asian, and Hispanic patients with private insurance face significantly higher out-of-pocket maternity care costs compared to their White counterparts.

New research provides expert-backed guidelines on the safety, risks, and benefits of cold water swimming during pregnancy, helping expectant mothers make informed decisions.

A new study found that using tocolytic drugs after 30 weeks' gestation does not improve neonatal outcomes, challenging current preterm birth treatment practices.

A new study finds that a 1-hour oral glucose tolerance test is more effective than the traditional 2-hour test in predicting future diabetes risk, especially for women with a history of gestational diabetes.

A new study reveals that obstetrician-led lecture and simulation training significantly improve Emergency Medicine residents' comfort in managing complex obstetric conditions.

A recent study suggests that a higher Hepatic Steatosis Index in early pregnancy is linked to an increased risk of gestational hypertension and preeclampsia.

A multi-layer perceptron risk prediction model outperforms traditional methods in identifying high-risk pregnancies, offering a promising tool for early intervention.

Sonio’s artificial intelligence-powered model improves fetal anomaly detection by 22 points, enabling earlier diagnosis and better maternal-fetal health outcomes.