As we are now incorporating the new post-COVID-19 “normal” into our routines, our editor-in-chief, Dr. Catherine Spong, reflects on parallels with changes that went into play with the identification and management of patients with HIV.

As we are now incorporating the new post-COVID-19 “normal” into our routines, our editor-in-chief, Dr. Catherine Spong, reflects on parallels with changes that went into play with the identification and management of patients with HIV.

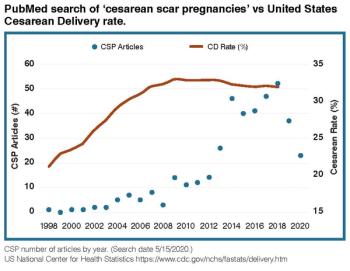
Cesarean scar pregnancy (CSP) is a complication in which an early pregnancy implants in the scar from a prior cesarean delivery. Incidence and recognition of this condition appear to have increased over the past two decades, perhaps due to high worldwide cesarean delivery rates. The clinical presentation is variable, and many women are asymptomatic at presentation. CSP can be difficult to diagnose in a timely fashion. Ultrasound is the primary imaging modality for CSP diagnosis. Expectantly managed CSP is associated with high rates of severe maternal morbidity such as hemorrhage, placenta accreta spectrum (PAS), and uterine rupture. Given these substantial risks, pregnancy termination is recommended after CSP diagnosis. Several surgical and medical treatments have been described for this disorder, but at this time, optimal management remains uncertain.

Cesarean scar pregnancy (CSP) is a complication in which an early pregnancy implants in the scar from a prior cesarean delivery. Incidence and recognition of this condition appear to have increased over the past two decades, perhaps due to high worldwide cesarean delivery rates. The clinical presentation is variable, and many women are asymptomatic at presentation. CSP can be difficult to diagnose in a timely fashion. Ultrasound is the primary imaging modality for CSP diagnosis. Expectantly managed CSP is associated with high rates of severe maternal morbidity such as hemorrhage, placenta accreta spectrum (PAS), and uterine rupture. Given these substantial risks, pregnancy termination is recommended after CSP diagnosis. Several surgical and medical treatments have been described for this disorder, but at this time, optimal management remains uncertain.

The patient had a history of fibroid uterus and dilated pelvic vessels in the left adnexal region, obscuring the left ovary. On April 2, 2014, the patient was seen as a gyn outpatient at the clinic by Defendant OB. The patient complained it caused her urinary tract irritative symptoms and back pain. An MRI was ordered for evaluation. A 9.9cm exophytic fibroid arising from the posterior uterine body with focal cystic degeneration was seen.

Behavioral methods of contraception are used by less than 3.2% of sexually active women; careful counseling could change that.

Would you be able to recognize this diagnosis in your practice?

Physical training can preserve and even significantly bolster the bone mass of the hip and femoral neck in individuals under caloric restriction, according to a systematic review and meta-analysis of 13 randomized clinical trials.

The timing of postmenopausal hormone therapy (HT) significantly impacts coronary risk and overall benefit-to-risk profile, according to an overview of Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) results in the journal Menopause.