
We've created a new app to enhance your reading experience with interactive features such as pop-out charts, videos that play in the app, and more. The app is free in the Apple iTunes store.

We've created a new app to enhance your reading experience with interactive features such as pop-out charts, videos that play in the app, and more. The app is free in the Apple iTunes store.

The latest results from the Women’s Health Initiative Hormone Trials provide new details on risks and benefits of therapy across age groups and time.

A population-based Canadian study suggests that young, female migraineurs are at increased risk of suicidal ideation, pointing to a need for their physicians to screen them for depression. The results, published in Depression Research and Treatment, were by researchers from the University of Toronto.

The use of metoclopramide to treat nausea during pregnancy is not associated with an increased risk of stillbirth, major congenital malformations, or spontaneous abortion, according to a recent study in JAMA.

Fertility treatment isn’t linked to an increased risk of ovarian cancer, according to a National Cancer Institute (NCI)-supported study spanning nearly two decades and published in Fertility and Sterility.

The ethical issues between two new technologies are stark. One aims to cure disease, whereas the other threatens to alter fundamentally the parent-child relationship.

New research confirms that use of metoclopramide, commonly used for nausea and vomiting, in early pregnancy does not increase risk of major malformations.

A 40-year longitudinal study of mother-adult offspring pairs suggests that mothers’ prenatal levels of glucocorticoids and smoking may be linked to their daughters’ smoking in adulthood. The report, published in Biological Psychiatry, is the first evidence linking prenatal glucocorticoid programming to adult nicotine dependence in daughters but not sons.

Motor vehicle accidents have long been linked to serious trauma during pregnancy, but a recent study published in American Journal of Preventive Medicine tied crashes to adverse pregnancy outcomes.


Preterm birth increases the risk of infant mortality and autism, but poor academic and social outcomes are likely caused by confounding factors and not preterm birth itself.

The FDA has approved Duavee, the first medication to combine estrogen with bazedoxifene, for the treatment of hot flashes and the prevention of osteoporosis after menopause.

Accelerated approval of Perjeta (pertuzumab) was granted by the FDA as part of a complete treatment regimen for patients with early stage breast cancer before surgery.
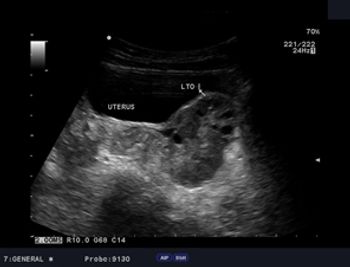
What is your diagnosis in this 7-year-old girl who presented with left pelvic pain?

To better balance the use of ultrasound and the time needed to ensure that an early pregnancy is not incorrectly declared nonviable, a group of experts have introduced new diagnostic thresholds.

The use of ice packs is an effective but nonstandard method of pain control after open abdominal surgery, and an experimental prolonged drug delivery system using nanotechnology is in the works.

The first drug combining estrogens with bazedoxifene has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of moderate-to-severe vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause and prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis.

Postmenopausal women who walk at least 7 hours per week have a significantly lower risk of breast cancer than their less active counterparts. Those are the findings of a large epidemiologic study published in Cancer: Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention.

A new study in Anesthesia & Analgesia indicates that the incidence of severe and fatal sepsis during labor and delivery is on the rise in the United States.

Abuse inflicted during childhood is lasting. Remember that adult patients may be survivors of child abuse, which makes them at risk for being in abusive relationships and for abusing their own children.

The outcomes of infants with poor fetal growth are better than what has been historically reported, according to preliminary study results.
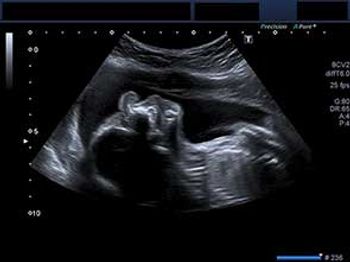
What is your diagnosis of this facial anomaly in a 24-week fetus?

Evidence indicates that angiogenic growth factors have an important role in fibroid pathophysiology, including abnormal vasculature and fibroid growth and survival.

Breast density laws ensure that women receive critical breast-health information, supporters say, but many of the laws broadly classify breast density and fail to account for varying levels of risk.

Teens who eat peanut butter and other nuts may be at lower risk of benign breast disease (BBD) as adults, according to a new report published in Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.

A new retrospective study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology shows that robotics don’t improve benign hysterectomy outcomes and, in fact, increase cost of the surgery.

Robotic-assisted laparoscopic myomectomy and abdominal myomectomy to manage uterine fibroids were equally effective in improving symptoms, but each procedure has its own benefits.

Clear, consistent steps for each specific surgical procedure should be adopted so that team members can become familiar with each procedure with repetition. Procedural steps for a robotic hysterectomy are shown in the video.

A commentary on ACOG Practice Bulletin Number 133: Benefits and risks of sterilization

We all know that American healthcare technology is expensive. But is it worth it?