
Merck earned a new indication for pembrolizumab (Keytruda), in combination with chemotherapy, to treat locally recurrent unresectable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).

Merck earned a new indication for pembrolizumab (Keytruda), in combination with chemotherapy, to treat locally recurrent unresectable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Study shows implementing the newly cleared software can slightly improve sensitivity and false negatives.

From OncLive, five experts share their perspectives and opinions on the latest research related to triple-negative breast cancer.
In a recent video from OncLive, Erika P. Hamilton, MD, highlights the initial findings from the ongoing phase 1b/2 LIO-trial in advanced metastatic tumors.
According to new research, women with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) are more than three times as likely to suffer from breast cancer mortality than women in the general population.

Officials from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a safety alert on Sept. 8 about potential efficacy and safety concerns with Tecentriq in combination with Paclitaxel for breast cancer treatment.
Results from the study showed antitumor activity and safety to be similar to olaparib and durvalumab monotherapy outcomes.
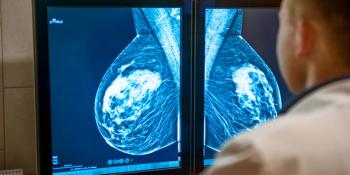
According to the findings, mammograms declined by 89.2% in April of this year.

Findings from a new study by Australian researchers suggest that physical activity should be incorporated into cancer care during and beyond treatment.
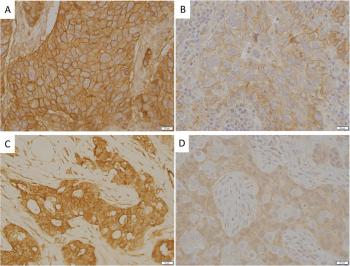
The lack of data on the possible connection between race and breast cancer prognosis is what led a group of Mount Sinai researchers to conduct this new multicenter, cross-sectional study.
A study from the Long Island Breast Cancer Study Project (LIBCSP) investigated the association between menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) and mortality outcomes among breast cancer survivors.

New research shows that, when seeking treatment for cancer-related fatigue, breast cancer survivors underutilize recommendations.

The study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology is a follow-up to a study conducted by the same authors to evaluate if pregnancy is safe in breast cancer patients who have hormone-sensitive breast cancer.
According to a new study in the American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy, chemotherapy stewardship programs may result in cost savings to both patient and health systems.
Women with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) may experience higher risk of developing invasive breast cancer (IBC) and of death from breast cancer than the general population, according to new research.

New research shows that, in postmenopausal women undergoing hormone therapy for breast cancer, aromatase inhibitors (AIs) lead to a reduction in climacteric symptoms and significantly improved quality of life.
The review concluded that the highest increase in MD is among current users of HRT, particularly those taking continuous estrogen plus progestin (CEP).
Currently, 38 states and the District of Columbia have enacted dense breast notification (DBN) laws mandating that mammogram results include language informing women of risks related to dense breasts.
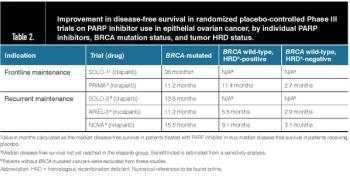
Across different drugs and clinical settings, use of PARPi has resulted in a prolonged period without cancer recurrence.

In recent years, the United States has seen a shift in greater awareness of the importance of SDOH and toward a more comprehensive approach to healthcare.

New research indicates that women may be able to reduce menopausal symptoms by increasing their intake of fruits and vegetables (FV).
Findings from a new study show significant overall survival benefit of Novartis’ ribociclib in hormone receptor positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 negative (HR+/HER2-) advanced or metastatic breast cancer with visceral metastases.

Australian researchers believe that PD-L1 may have potential as an indicator of potential response to chemotherapy in women with metastatic breast cancer. That was based on results of a randomized trial, presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology in Lugano, Switzerland.
The results show that participating in screening mammography is essential for reducing the number of deaths from breast cancer and can ultimately save lives through early detection.
Long-term adherence improvements, it appears, require personalized and sustained behavioral interventions. TMs for AI should also be personalized for individual success.