
Uterine fibroid is a slowly growing benign smooth muscle tumor. Approximately 25% of women after the age of 35 years harbor uterine fibroid. Most of these women are asymptomatic and in general, they do not need any treatment

Uterine fibroid is a slowly growing benign smooth muscle tumor. Approximately 25% of women after the age of 35 years harbor uterine fibroid. Most of these women are asymptomatic and in general, they do not need any treatment

Currently there are two ways to treat endometriosis – hormonal therapy and surgery. Depending on the patient’s expectations and the extent of the disease, we may prescribe hormonal therapy, surgery, a combination of surgery and hormonal therapy, or occasionally a just “wait and see” approach.

Tubal sterilization is the method of family planning most commonly used. The existence of the post-tubal-ligation syndrome of menstrual abnormalities has been the subject of debate for decades.

The most important question to ask is whether or not the fibroids need to be treated at all. The vast majority of fibroids grow as a woman gets older, and tend to shrink after menopause. Obviously, fibroids that are causing significant symptoms need treatment. While it is often easier to treat smaller fibroids than larger ones, many of the small fibroids never will need to be treated. So just because we can treat fibroids while they are small, it doesn't follow that we should treat them. The location of the fibroids plays a strong influence on how to approach them. A gynecologist experienced in the treatment of fibroids can help you determine if they need to be treated.

Fibroids are non-cancerous (benign) growths of the muscle wall of the uterus. They are probably responsible for more unnecessary gynecologic surgery than any other condition. It is a staggering number, but about 600,000 American women have a hysterectomy every year. And about 30% of those hysterectomies, 180,000 in all, are performed because of fibroids. For many years these growths have been surgically removed, often because of fear of the problems they might cause in the future. And, those problems are often overstated. While approximately 30% of all women will have fibroids during their lifetimes, the vast majority of these women will never have symptoms and will never require treatment. And, for the rare patient that does have problems, there are a number of sound and effective options available. Hysterectomy should be the solution of last resort.

Throughout history, menstruation has been associated with myth and superstition. Menstrual blood was felt to cure leprosy, warts, birthmarks, gout, worms and epilepsy. It has been used to ward off demons and evil spirits. Menstruating women have been separated from their tribes in order to prevent a bad influence on the crops or the hunt. As recently as 1930, the cause of abnormal menstrual bleeding was felt to be an undue exposure to cold or wet just prior to the beginning of the period.

The terminology used to describe pap smear results has changed over the past few years, leading to confusion about what the results of your pap smear actually mean. Originally, pap smears were divided into 5 "classes" based on what the cells looked like to the pathologist. Class I was normal, while class II cells appeared a little irregular to the pathologist, usually representing bacterial infection. Class III and IV pap smears suggested that dysplastic cells were present, and further testing needed to be done. Class V usually meant cancer.

Over the past decade, a technique has been developed that can reduce or stop your periods without a hysterectomy. This surgery can be done in women who have flooding either with or without fibroid tumors. Dr. Dott was one of the surgeons who introduced this minimally invasive procedure in Atlanta. He has performed this procedure many times and is certified by the Accreditation Council for Gynecological Endoscopy in Advanced Hysteroscopic Surgery. He has taught this procedure in training institutions both in the United States and Russia.

Chronic pelvic pain (CPP) is often accompanied by poorly defined symptoms and a sense of failure by both doctor and patient.

Laparoscopy, looking inside the abdomen through a tube placed through a small incision, is a procedure commonly used by gynecologists to diagnose and treat a number of medical conditions. Since the early 1900's when rudimentary laparoscopes were used to visualize, but not treat, abdominal diseases, advancements in this technique have led to the ability to perform complex surgical procedures through a few small incisions, rather than the larger incisions used in the past.

Uterine fibroids ( "fibroid tumors";" leiomyoma"; "myomas") are benign, (non-cancerous) growths present in about 30% of women over the age of 30. They are usually detected on pelvic examination, which may reveal the uterus to be enlarged and/or irregular in configuration. The vast majority of cases are absolutely silent and cause no symptoms. The size of a single fibroid may be smaller than a pea, or larger than a melon. In a given patient, there may be a single fibroid, or multiple fibroids of varying size. In the latter situation, the summation of the fibroids of varying sizes will lead to an aggregate size increase.

"Abnormal Uterine Bleeding" or "AUB" is a relatively common condition. Normal menstrual flow produces less than 3 ounces of blood, in a maximum of 7 days. AUB patterns are characterized by flows that are heavier, and/or more prolonged or more frequent than a 21-28 day interval. AUB can cause anemia, embarrassment, or marked inconvenience. It has been said by many so afflicted women-" I have to plan my life around my period".

Hysteroscopy is a form of minimally invasive surgery. The surgeon inserts a tiny telescope (hysteroscope) through the cervix into the uterus. The hysteroscope allows the surgeon to visualize the inside of the uterine cavity on a video monitor. The uterine cavity is then inspected for any abnormality. The surgeon examines the shape of the uterus, the lining of the uterus and looks for any evidence of intrauterine pathology (fibroids or polyps). The surgeon also attempts to visualize the openings to the fallopian tubes (tubal ostia).
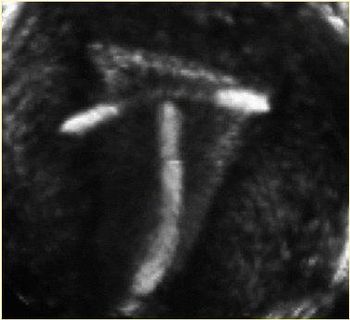

At the time I was starting this blog two patients with similar fibroids came to see me. Both were severely anemic, and one was hemorrhaging and in shock.

More than half of the 600,000 hysterectomies performed in the 1900s involved bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and it has been estimated that many of those were performed solely to reduce the risk for ovarian cancer. While there has been increased knowledge in the risk in women with familial history, a knowledge gap still exists for other women, which could lead them down the path of potentially unnecessary surgery

A recent survey found that US ob/gyn residents need more education about the benefits of the IUD in addition to evidence-based recommendations for IUD candidate selection.

Intrauterine devices (IUDs) represent a safe and effective option for preventing unwanted pregnancies. Yet studies have shown that gynecologists still have concerns over its safety and do not utilize evidence-based criteria to assist in the selection of IUD candidates. In order to overcome this obstacle, it is imperative that current obstetric and gynecology residents are receiving correct information on this treatment modality-but are they?

As clinicians and patients strive to find oral contraceptives that are safe and effective, newer varieties have emerged on the market. Venous thromboembolism, an adverse event that has been associated with third-generation oral contraceptives, is a serious concern, especially with the growing popularity of these newer contraceptives.

Untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in pregnancy can lead to such negative outcomes as spontaneous abortion, preterm birth, low birth weight, congenital infections, and other abnormalities.

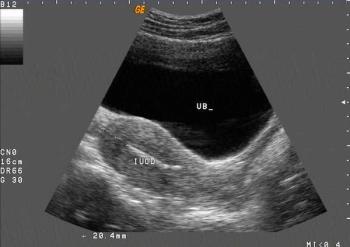
Incorrectly positioned intrauterine devices (IUDs) make intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) more likely, with more than half of IUDs identified during the first trimester of pregnancy malpositioned, according to a study published online Feb. 24 in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology.

Intrauterine devices (IUDs) can be a safe, effective, and relatively easy birth control option. However, pregnancy can occur if the IUD dislodges or is not placed properly. Dr Elysia Moschos, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology, and Dr Diane M. Twickler, professor of radiology, at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, studied ultrasound findings, clinical symptoms, and outcomes for women with first-trimester pregnancies despite having intrauterine devices to better understand this issue.

March 9, 2010 a 46 year old woman came to me having been told that she needs a hysterectomy because of heavy bleeding from her fibroid. She wanted to know her options. Ultrasound showed a tennis ball size fibroid that was 2/3 in the uterine wall and 1/3 in the cavity of the uterus.

Teen birth rates in the United States have declined over the last two decades, but they remain high, according a Vital Signs report in the April 5 early-release issue of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.