The ever-use of an intrauterine device (IUD) reduces the risk of ovarian cancer by an average of 30%, according to a rigorous meta-analysis in the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.

The ever-use of an intrauterine device (IUD) reduces the risk of ovarian cancer by an average of 30%, according to a rigorous meta-analysis in the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.
Pregnant women with autoimmune-related interstitial lung disease (ILD) can have safe pregnancy outcomes if closely monitored by a multidisciplinary team of physicians.

An analysis of CDC data presented at American Heart Association's Scientific Sessions 2020 suggests rates of high blood pressure complications during pregnancy nearly doubled during a period lasting from 2008-2017.

Findings from a retrospective study by researchers from NYU suggest that women with COVID-19 in pregnancy have an increased risk of placental abnormalities, regardless of whether their infection is symptomatic.

November is Prematurity Awareness Month. Here are a few quick facts.

New research suggests that postpartum depression may persist for 3 years following birth.

New research suggests that air pollutant particles and metals are reaching the placenta.
Despite the fact that extended newborn screenings have been used for more than 20 years, the impact of such screenings on long-term clinical outcomes among individuals who had inherited metabolic diseases is still relatively unknown.

Each year, approximately 24,000 babies are stillborn in the U.S, and as many as half of all pregnancies may end in miscarriage.

New research suggests that placental DNA may have potential as a biomarker for adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs).

The risk of venous thromboembolism is particularly high during the postpartum period and especially following cesarean delivery.

Effective treatment will depend on the diagnosis, but can range from simple to very complex.
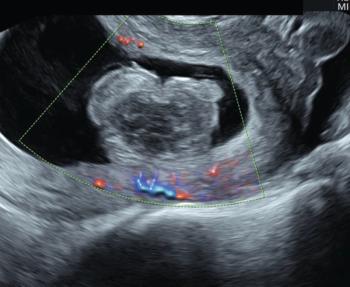
Ultrasound technology can be an indispensable tool for the management of suspected early pregnancy loss.
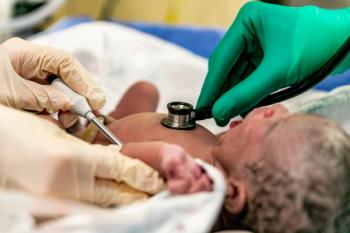
Although previous research has shown preterm (PTB) and post-term births to result in adverse neuropsychiatric outcomes in children little research had been done on the outcomes of at-term deliveries.
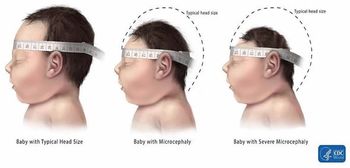
A new study in JAMA Pediatrics analyzed the number of microcephaly cases that resulted from congenital microcephaly and how it may be a larger cause than the 2016 Zika epidemic.

A new study published in JAMA Network Open investigated whether perinatal depression and/or anxiety impacted childhood development.

The following points summarize information from a Joint Statement of the Perinatal Quality Foundation, ACMG, ACOG, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM), and the National Society of Genetic Counselors on “points to consider” when performing expanded carrier screening in reproductive medicine.

A new study by French investigators shows that adenomyosis confined to the outer myometrium is associated with primary infertility—but not more diffuse disease.

Halley Crissman, MD, MPH, and Daphna Stroumsa, MD, MPH, MSC, discuss ways in which ob/gyns can provide high-quality care for transgender and nonbinary people assigned female sex at birth.
Expanded carrier screening addresses limitations in historical ethnic-based screenings, including potential racial and ethnic bias.

This peer-reviewed article discusses the main causes of infertility, including tubal disease, uterine factor, cervical factor, and ovulatory dysfunction and anovulation.

As detailed in the September issue, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM) is highlighting one of these situations: the role of activity restriction in obstetric management.

Little evidence supports the routine use of activity restriction for preterm birth and other obstetric conditions, and some data indicate adverse impact on obstetric outcomes.

Pregnant patients learning to navigate the world of genetic health now have access to an app that helps to explain chromosomes, conditions that prenatal screening can identify, and available testing options such as non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT).

The authors reviewed studies with primary outcomes that were factors associated with unsuccessful pessary fitting and discontinuation in women with POP and 21 for final analysis.