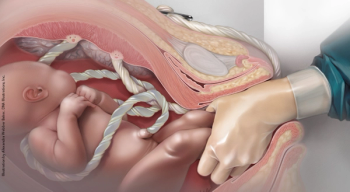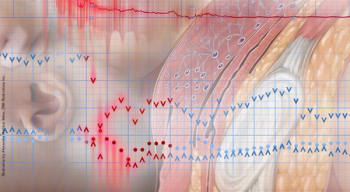
A recent study looked at which approach to second-stage labor results in higher spontaneous vaginal delivery rates and lower rates of maternal and neonatal complications. PLUS: What makes hospitals safe for mothers and babies? ALSO: Does eating meat increase risk for breast cancer?