Pregnancy and Birth
Latest News
CME Content


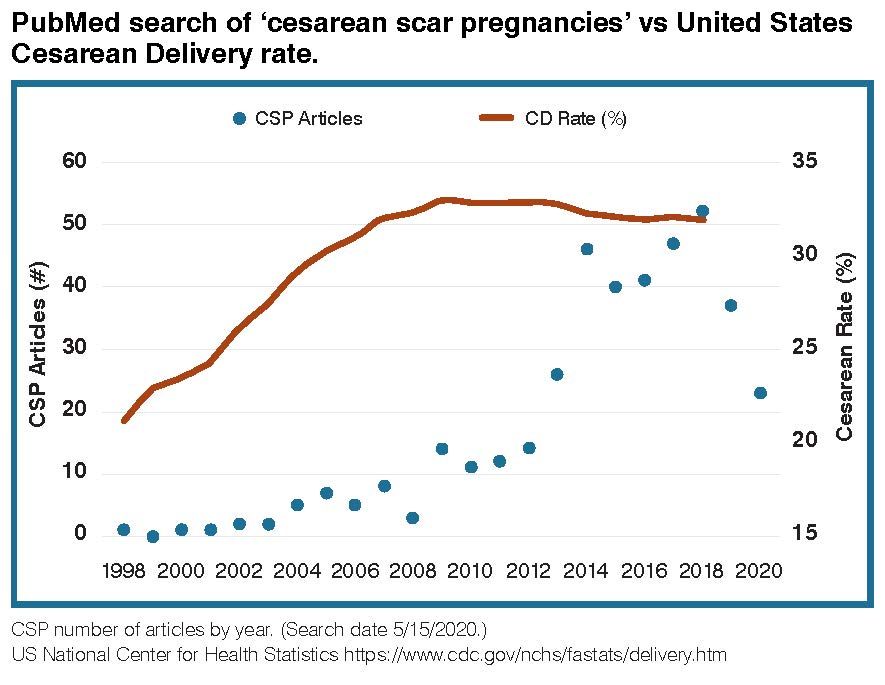
Cesarean scar pregnancy (CSP) is a complication in which an early pregnancy implants in the scar from a prior cesarean delivery. Incidence and recognition of this condition appear to have increased over the past two decades, perhaps due to high worldwide cesarean delivery rates. The clinical presentation is variable, and many women are asymptomatic at presentation. CSP can be difficult to diagnose in a timely fashion. Ultrasound is the primary imaging modality for CSP diagnosis. Expectantly managed CSP is associated with high rates of severe maternal morbidity such as hemorrhage, placenta accreta spectrum (PAS), and uterine rupture. Given these substantial risks, pregnancy termination is recommended after CSP diagnosis. Several surgical and medical treatments have been described for this disorder, but at this time, optimal management remains uncertain.

Specific interventions may be needed in pregnancy to promote early offspring psychopathology health and wellbeing.

The most common electrolyte abnormality seen in infants with jitteriness is hypoglycemia.

Early-life predictors are crucial for continued development of effective preventive strategies for T2DM.

Risk of labor induction and cesarean delivery is increased in nulliparas who are obese, and use of misoprostol or insertion of a Foley balloon often fails in these patients, for reasons that aren’t fully understood.


Jamie Barretto is a 34-year-old first-time mother who lives on Long Island. She wrote this first-person perspective on how life has changed in her world since she found out she was expecting in October.
In this video interview, Senior Editor Angie DeRosa talks with Dr. Kristina Adams-Waldorf, Professor in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Adjunct Professor in Global Health at the University of Washington (UW) School of Medicine in Seattle.

New research by Finnish investigators shows a significant link between maternal hypertension and mental health disorders in children.
New research suggests that certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as Trichomonas vaginalis and Neisseria gonorrhea, may contribute to a higher risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes and preterm birth (PTB) in adolescents.
Rates of vaginal birth after cesarean (VBAC) in the United States are on the rise, but the Healthy People 2020 goal for the marker-18.3%-isn’t likely to be reached for another 10 years, according to a new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).

The National Institutes of Health has released a comprehensive set of guidelines for the treatment of COVID-19, which includes recommendations for the care of pregnant women.
Contemporary OB/GYN Senior Editor Angie DeRosa interviews Dr. Laura Riley, MD, a renowned obstetrician who specializes in obstetric infectious disease. Dr. Riley weighs in on COVID-19.

A study published in The Lancet explored which and to what degree prenatal and perinatal factors are associated with later onset of psychosis.

New research from Pediatrics suggests that nativity and country of education are predictors of breastfeeding and should be assessed in postpartum settings to encourage breastfeeding support.
A large-scale clinical trial of dietary supplementation in couples being treated for infertility shows that taking folic acid and zinc does not increase sperm quality or live birth rates

Results of a new Scottish study suggest that delivery after 37 weeks’ gestation is optimal for uncomplicated twin pregnancies.

As the impact of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic continues to escalate, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM) has released guidance on the maternal, fetal and neonatal implications of the disease.

Finnish researchers say that maternal smoking during pregnancy leads to reduced infant body length and head circumference, effects that remain unchanged even if a woman stops smoking during the first trimester.

Women with depression are more than three times more likely to use cannabis while pregnant, according to a recent study from Drug and Alcohol Dependence.

In this video, Jon Einarsson, MD, PhD MPH, discusses his work to develop a less invasive technique for removal of the transmural bowel nodules.

New research indicates that unintended pregnancy is much more likely in women with than without disabilities

In-depth interviews with program administrators in Texas show that changes to Title X are decreasing access to services for teens and the quality of those services.

An analysis of Twitter postings shows that celebrity disclosures help drive discussions about pregnancy complications on social media.