
A new study released by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) indicates that opioid use in women may result in higher chances of pregnancy loss and lower chances of conceiving.

A new study released by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) indicates that opioid use in women may result in higher chances of pregnancy loss and lower chances of conceiving.

Hear Her aims to raise awareness of pregnancy-related deaths and provide support and education to pregnant women and postpartum women (within 1 year of delivery).
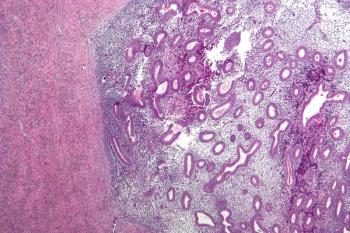
Researchers sought to investigate the effects of endometrioma and the impact of bilaterality on in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) outcomes.
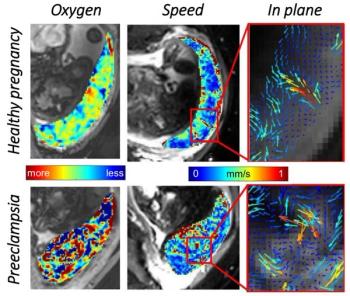
A new study offers important new insights into various placental functions and describes a new physiological phenomenon.
A literature review in Pediatrics sought to understand more about the possible impacts.
A literature review published in Pediatrics analyzed whether the practice of immunizations during pregnancy influence other early health outcomes.

A new study in the New England Journal of Medicine investigated the joint effect of gestational age and Apgar scores on the risks of neonatal death.
A new report in Pediatrics investigated whether black children were likely to have more complications and greater mortality following surgery than their white peers.

The results of this study allowed researchers to identify the onset mechanism of recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL), especially in some cases that would have otherwise remained unexplained.
A new study from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) may shed light on why the virus has rarely been found in fetuses and newborns of mothers infected with COVID-19.

A recent systematic review found that climate change-related exacerbation of the two exposures may be having an adverse effect on obstetric outcomes.

This episode of Pap Talk by Contemporary OB/GYN features an interview with Dr. Kristina Adams-Waldorf, Professor in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Adjunct Professor in Global Health at the University of Washington (UW) School of Medicine in Seattle.

This episode of Pap Talk by Contemporary OB/GYN features an interview with Dr. Emily S. Miller, with Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.

Two calculators for practitioners to estimate fetal growth percentiles, velocity and account for racial and ethnic variation from the NICHD are now available.

In the United States, marijuana use by adults has increased in recent years.

Data on COVID-19 during pregnancy, as reported by the CDC, in collaboration with state, local, and territorial health departments and external partners.
A nationwide study by Swedish researchers suggests that inducing labor at no later than 41 weeks could be one of the few interventions that reduce stillbirths.

For Cord Blood Awareness Month, here are some updated usages and FDA regulations for practitioners using cord blood.

Data on COVID-19 during pregnancy, as reported by the CDC, in collaboration with state, local, and territorial health departments and external partners.
NICU utilization trends have yet to be thoroughly investigated.
The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) updated its list of demographics at higher risk for COVID-19, due to new evidence.

A new report in Archives of Disease in Children examined the rates of sudden unexpected death in infancy (SUDI) among families that occurred after a previous incident of SUDI.

Telehealth has made its way into many ob/gyn practices. With many patients hesitant to visit their doctors in person, it may be difficult to convince them to schedule in-person visits.
Rates of depression at 6 weeks postpartum among adolescents and young adults (AYA) were significantly lower in those initiating immediate postpartum etonogestrel (ENG) implants compared to other birth control methods, according to new research.

June 19, 1865, also known as Juneteenth, celebrates the end of slavery in the United States. On this day nearly 160 years ago, Union troops arrived in Galveston, TX to announce the end of the Civil War and the emancipation of slavery in the United States.