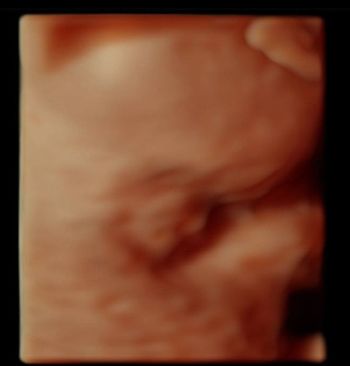
Challenge your anatomy knowledge; what body part is this 3-D image showing?

Many sexual desire problems in women can be addressed without a prescription, but OB/GYNs must first develop skills for frank discussions with patients about sex.

An intensive in-home program aimed at pregnant teens at risk for drug use and depression, specifically American Indian teens, proves successful.

When evaluating vasomotor symptoms in menopause, including sleep-wake cycles, have you ever considered the utility of an activity tracker?

Here's one way to attract new patients from a younger demographic.
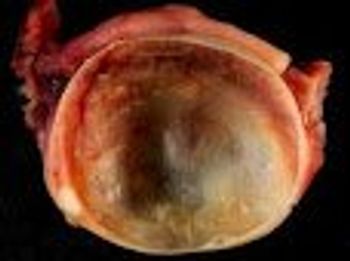
New research looking at complication rates and cost for oophorectomy and cystectomy favors conventional laparoscopy over robotic surgery.

A new mobile app is now available to help women and their providers make decisions about managing symptoms related to menopause.

Women who consume fried foods more than 7 times a week pre-pregnancy are more likely to have gestational diabetes when they become pregnant.

An analysis of data from nearly 90,000 women who underwent adnexal surgery over a 3-year period shows that robotically assisted procedures were associated with substantially higher costs and increases in intraoperative complications.

Adopting and adhering to a low-risk, healthy lifestyle before pregnancy is associated with a low risk of gestational diabetes and could be an effective way to prevent the complication, according to a new study in the BMJ.

According to a recent study, low-dose oral bisphosphonates administered to prevent or treat postmenopausal osteoporosis may be associated with a lower risk of skeletal metastasis in patients with early- or more advanced-stage breast cancer.

Don't overpromise when it comes to elective egg freezing. It doesn't protect against infertility nor does it guarantee a future pregnancy.

Experts advise against any off-label prescribing of testosterone for women, unless they are postmenopausal with a low sex drive.
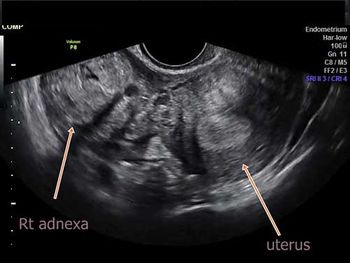
Challenge your diagnostic skills with these images from a young woman with right pelvic pain and a history of amenorrhea.
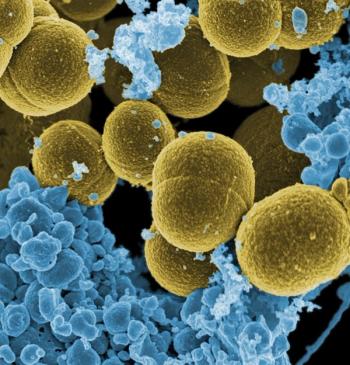
Researchers have developed a "biospleen"-a device that could filter unknown pathogens from the blood in patients at risk for sepsis.
Despite the prevalence of the procedure, there is no proven best way to prevent surgical site infections related to cesarean sections.

How's this for wishful thinking to explain an extremely active fetus?

Not enough medicine or not enough ethics? Paul Burcher, MD, PhD, shares his thoughts on finding the balance for good medical ethical decision making.

A large, prospective study shows that teens ages 15 to 19 will use choose and use long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs) when they are educated about those methods and given them at no cost.

Women who become pregnant again within a year of birth or more than 5 years later may be at increased risk of having a child with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), according to a recent study.

Results from a study of nearly 100,000 women suggest that increasing skirt size over a lifetime--a proxy for waist circumference-may be an indicator of increased risk of postmenopausal breast cancer.

Menopause will be unique for each woman, and a physician-patient partnership is a must if women want effective menopause management.
Challenge your diagnostic skills with these images of a third trimester pregnancy. Can you identify the "incidental" findings?
People like free stuff, especially teenagers. And if you give them free birth control, particularly LARC, they tend to use it.


Osteoporosis isn't a disease of older women; it's a disease of all women, incubating in even our youngest patients.

New data highlights the importance of 3 key behaviors of all women of reproductive age for preventing gestational diabetes.

According to a recent study in Fertility and Sterility, assisted reproductive technology (ART) does not increase the risk of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children conceived using the technology.

According to a recent study in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, the evidence continues to mount for an association between breastfeeding and reduced risk of aggressive breast cancers in African-American women.

A computerized decision-support guide may help women make more informed choices about prenatal testing, according to results of a randomized trial published in JAMA. The findings, which require validation in other populations, suggest that, were women better educated about the technology, fewer prenatal tests would be done.