
The best first- and second-line therapies for vulvovaginal atrophy are highlighted in an updated position statement from The North American Menopause Society.

The best first- and second-line therapies for vulvovaginal atrophy are highlighted in an updated position statement from The North American Menopause Society.

Recent findings by the World Health Organization (WHO) show that around the world, life expectancy for women over age 50 is still increasing.

In 2010, Medicaid financed 48% of all births in the United States, an increase of 19% in the proportion of all births covered by Medicaid in 2008. This finding, from a study published in the Sept. 2013 issue of the journal Women's Health Issues, adds to previous research showing that the numbers of women dependent on Medicaid for health care are growing.

Estrogen therapy is still the mainstay of therapy for moderate-to-severe symptoms and long-term studies on endometrial safety of local estrogen and ospemifene are lacking. Those are the key conclusions from an updated position statement on management of symptomatic vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA) in postmenopausal women issued by the North American Menopause Society (NAMS).

The consumption of green tea extract has been shown to significantly reduce the size of uterine fibroids and improve symptom severity, a small study reported.

The use of an enhanced recovery pathway for perioperative care in complex gynecological surgery can reduce length of hospital stay, need for narcotic pain control, and costs.

To properly measure risk, the author argues, researchers must compare 1 twin pregnancy with 2 consecutive singleton pregnancies.

There is no evidence that UCP can be prevented, but rapid diagnosis and delivery have been shown to be advantageous. The authors present a plan to help you respond surely and swiftly.

The epidemiology of racial disparity in prematurity and infant mortality is a complex problem, say the authors, and public health programs are part of the solution.

The transition to ICD-10 is looming. You'll be ready if you start planning now.

The Contemporary OB/GYN tech experts address the learning curve associated with an EHR adoption.

Better communication between surgeons and pathologists will help to inform understanding of vaginal mesh complications.

The resection was not planned, consented to, or indicated, and this was enough reason to reach a settlement in this case rather than allow a jury to price it.

An innovative, individualized vaccine that may prolong the remission period of ovarian cancer survivors has been developed. Will it work?

The use of weighted vaginal cones for stress urinary incontinence is more effective than no treatment at all, the evidence shows.

A new index using protein markers can identify ovarian cancer cases at high and low risk for recurrence and discriminate between short- and long-term survivors.

A recent study in Nursing Outlook suggests that women who are responsible for full-time care of their grandchildren may be at increased risk of developing depressive symptoms compared with their non-primary caregiver counterparts.

A screening protocol that takes into consideration CA-125 levels over time and results of transvaginal ultrasound (TVS) shows promise in early detection of ovarian cancer, according to a new report from investigators at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. In a large, prospective study, the combination demonstrated excellent specificity and positive predictive value (PPV) in a group of women at average risk of ovarian cancer.

Enhanced recovery pathway (ERP) leads to earlier discharge, cost savings, better patient satisfaction, lower narcotic use, and more stable readmission rates in complex gynecologic surgery patients, according to a study recently published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.

Evidence shows that acupuncture seems to be the most effective intervention for preventing and treating pregnancy-related pelvic and back pain.
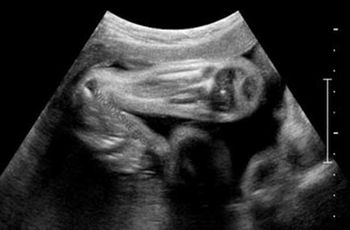
What is your diagnosis in this 3rd trimester fetus? Choose one from the following:

Vasomotor symptoms related to perimenopause and menopause in sedentary women are not alleviated by exercise, according to the results of a randomized controlled trial from the MsFLASH Research Network.

The percentage of married women aged 15–44 who were infertile fell from 8.5% in 1982 (2.4 million women) to 6.0% (1.5 million) in 2006–2010, according to a new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).

Looking for OB/GYNs on Twitter? Here’s a round-up of those who are worth a follow.

A recent study published in The Lancet Oncology looked at the likelihood of survivors developing arm lymphedema and found that roughly 20% of breast cancer survivors were likely to develop the condition.

Mobile healthcare apps and devices are expected to grow at a rate of 61% a year, with 50% of healthcare professionals using at least one app. Ob/gyns are leading the charge, and these 8 apps are helping MDs and HCPs manage patients and stay current on everything happening in the field.

Researchers suggest that recommendations for the universal screening of breast cancer with mammography be reassessed.

Depression over an extended period may make it more difficult for women to get pregnant.

Autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) have become more prevalent, with 1 in 88 children now being diagnosed, and scientists and parents want to know what may be causing the problem. Environmental factors’ impact on risk has been of significant interest. A study recently published in JAMA Pediatrics looks at the potential effect of induced labor on autism risk.

A round-up of OB/GYN Twitter accounts that are worth a follow.