Our malpractice lawyer counsels on a complicated case involving a delivery with an unexpected outcome and multiple health care providers involved.

Our malpractice lawyer counsels on a complicated case involving a delivery with an unexpected outcome and multiple health care providers involved.

A positive relationship appears to exist between the length of time a mother spends breastfeeding and language and intelligence when a child is older, a new study published online on July 29 in JAMA shows.

Bisphenol-A (BPA) has been making headlines for potential connections with neurologic conditions, obesity, and myriad other health concerns. A recent study published in Human Reproduction looked at whether BPA had a negative impact on fertility.

If sleep is interrupted, it may interfere with normal immune system functioning and lead to unwanted pregnancy outcomes. In addition, depression may play a role in how sleep affects the immune system. These findings were reported in Psychosomatic Medicine.

With 64% of pregnant women in the U.S. taking at least one medication during pregnancy, experts are arguing that it’s unethical not to include them in the testing of new drugs.

There is little difference in the effectiveness and safety of laparoendoscopic single-site surgery and conventional laparoscopic surgery for the treatment of gynecological diseases.
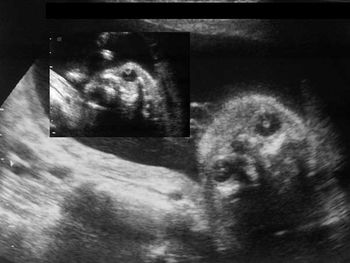
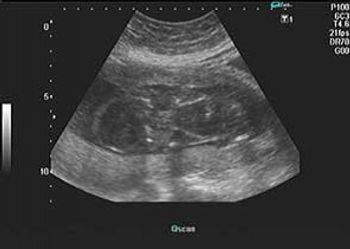
Ultrasound images of the fetal face and eyes are shown below. What is your diagnosis?

According to a recent report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there was a 5-fold rise in deaths of women who abused prescription opioid pain medicine from 1999 to 2010 (6631 deaths in 2010, up from 1287 in 1999).

Properly timing subsequent pregnancies is important for both mothers and babies. It’s often accomplished with postpartum contraception, which may be out of reach for low-income women. A recent study in Obstetrics & Gynecology looked at how prescription of postpartum contraception through publicly funded programs affects the interval between pregnancies.

An ob/gyn neglects to follow a molar pregnancy to its conclusion and the patient develops choriocarcinoma. A jury found in favor of the plaintiff.

In his August 2013 editorial, editor in chief Dr. Charles Lockwood discusses recent findings that obese women have a higher risk of extremely early preterm delivery.

A commentary on some of the best research in this field published in the past year

Obstetricians often see pregnant patients with psychiatric disorders, the most common being depression. Treatment includes both nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic options. This article focuses on use of selective serotonin reputake inhibitors (SSRIs), the drugs most often used to treat depression in pregnancy.

Your guide to determining appropriate candidates and appropriate routes of hysterectomy for benign gynecologic conditions

Retinoids may have some effect on regression of certain grades of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) but do not prevent disease progression.
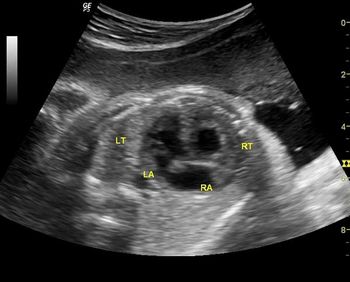
What is your diagnosis based on these images?

Women with a history of cancer are nearly twice as likely to experience severe menopausal symptoms, according to the results of a new study.

A therapy for Down syndrome may be just around the corner, thanks to scientists’ success in altering a genetic fault in isolated cells that ultimately leads to the condition, according to new study findings in Nature.

Incidence of gastroschisis among newborns appears to be on the rise, with the proportion of babies born with the rare defect almost doubling since 1995, new research shows.

When it comes to securing and protecting patient health information, physician practices with fewer than 50 providers fared the worst in a recent audit by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ Office for Civil Rights (OCR).

Research shows that vaccinating all teens-both boys and girls--results in an enormous reduction in HPV-related infections. Why aren't we doing it in the United States?
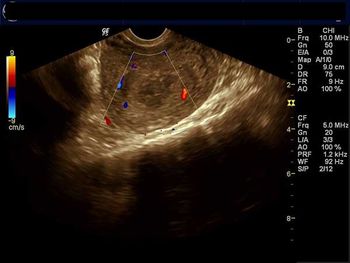
This middle-aged woman has a history of dysmenorrhea. What is your diagnosis based on these images?

After minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery, gum chewing has beneficial effects on bowel motility when used as an adjunct treatment in postoperative care, according to the results of a randomized controlled trial.

Despite new screening guidelines, most obstetrician-gynecologists continue to perform annual pap tests, according to a recent survey of members of the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG).

The common practice of clamping an umbilical cord within a minute of birth to reduce the possibility of maternal hemorrhaging may need to be revised, according to a new paper published in The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. The study authors searched the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group’s Trials Register to find 15 trials involving a total of 3911 mother and infant pairs. The risk of bias in the trials was considered by the paper’s authors to be moderate in nature.

If women are prediabetic when giving birth, they may find it difficult to make enough breast milk to feed their newborns, according to new research from Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center and the University of California, Davis. The findings show that insulin dysregulation can negatively impact milk supply.

With the October 1, 2014, deadline looming, many physicians are still struggling to get started in their adoption of the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10).

These beautiful and often other-worldly photographs by pathologist Ed Uthman, MD, show both benign and malignant ovarian pathology.

Prevention of maternal influenza during pregnancy may reduce the risk of bipolar disorder, suggest new study findings published in JAMA Psychiatry.