
Analysis of data from more than 2.2 million vaginal deliveries shows that episiotomy declined between 2006 and 2012 and nonmedical factors may have been at play. The findings were published in a Research Letter in JAMA.

Analysis of data from more than 2.2 million vaginal deliveries shows that episiotomy declined between 2006 and 2012 and nonmedical factors may have been at play. The findings were published in a Research Letter in JAMA.
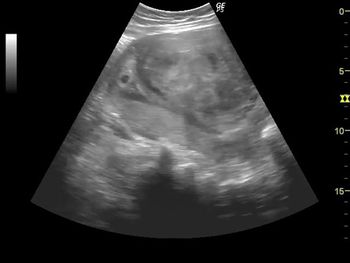
Challenge your diagnostic skills. What uterine-related findings are revealed in this pelvic scan?
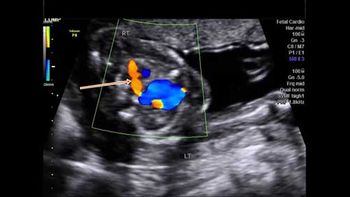
This 18-week fetus has a vascular anomaly. Can you identify it?
Can patients who desire a natural birth or vaginal delivery truly participate in shared decision making in a system of care that trends toward c-sections?

New research sheds light on how pregnancy can affect women with a mobility disability, such as a spinal cord injury or cerebral palsy.
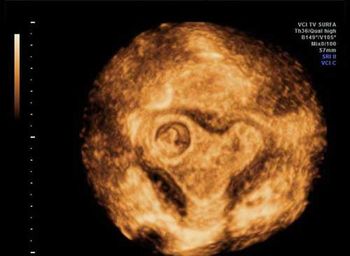
This uterus is anything but normal, but it still seems to function. What's your diagnosis?

For women with gestational diabetes, a low glycemic index diet was associated with less need for insulin and lower birth weights for the babies.

The request that makes every woman who's given birth and had an epidural for pain management chuckle-eventually.

A new recommendation for home birth or delivery at a birth center for certain women with uncomplicated pregnancies in the United Kingdom has been issued.

Maternal exposure to air pollution during pregnancy may be a contributing factor in the development of autism in offspring, new research shows.
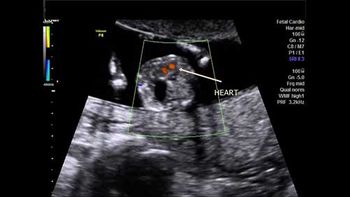
Challenge your diagnostic skills: What's your diagnosis based on these images from a 14-week fetus?

From surgical staplers to birthing simulator updates, 2014 brought many new innovations for obstetrics and gynecology.

Pink or blue? New research shows that low gestational weight gain early in the pregnancy is correlated with having a baby of a certain sex.
The good news is that Santa isn't pregnant. The bad news is that he may need to switch to reindeer food.
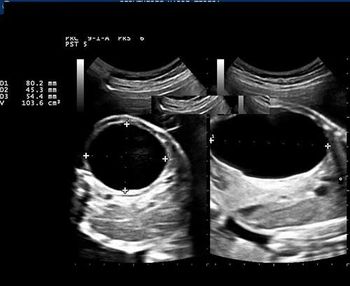
This image quiz focuses on the kidneys. Can you identify the abnormality seen in these ultrasound images of the fetal abdomen?

For those who focus so much on getting through the pregnancy that they forget to prepare for when baby comes home.

The FDA has granted a first-ever waiver for a rapid screening test for syphilis, allowing the test to be used in a greater variety of health care settings.

As obstetric units close and consolidate around the country, ways to improve interhospital communication and to assess patient outcomes are needed.
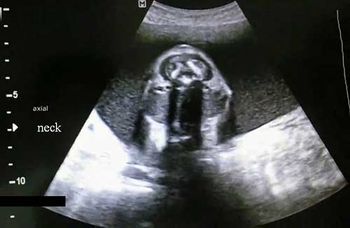
Challenge your diagnostic skills: Can you identify the condition causing the abnormality seen in these images of the fetal neck?

This cartoon highlights priorities, and what no OB wants-a third patient.

Be a broken record about the importance of folic acid supplementation. New research finds it is associated with fetal growth benefits.

The FDA says confusing labeling is out and now will provide safety data for medication use in pregnancy and breastfeeding in a relevant real-world context.
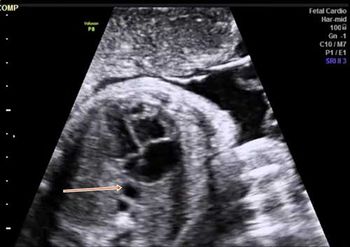
Challenge your anatomy skills: Can you identify the structure of interest in these images of the fetal thorax?

For women with congenital heart disease, the risk of pregnancy and delivery complications isn't as high as expected, new research shows.
Here's an example of what you don't see in your office; pregnancy pillows can be tricky!