Vulvovaginal Disease
Latest News
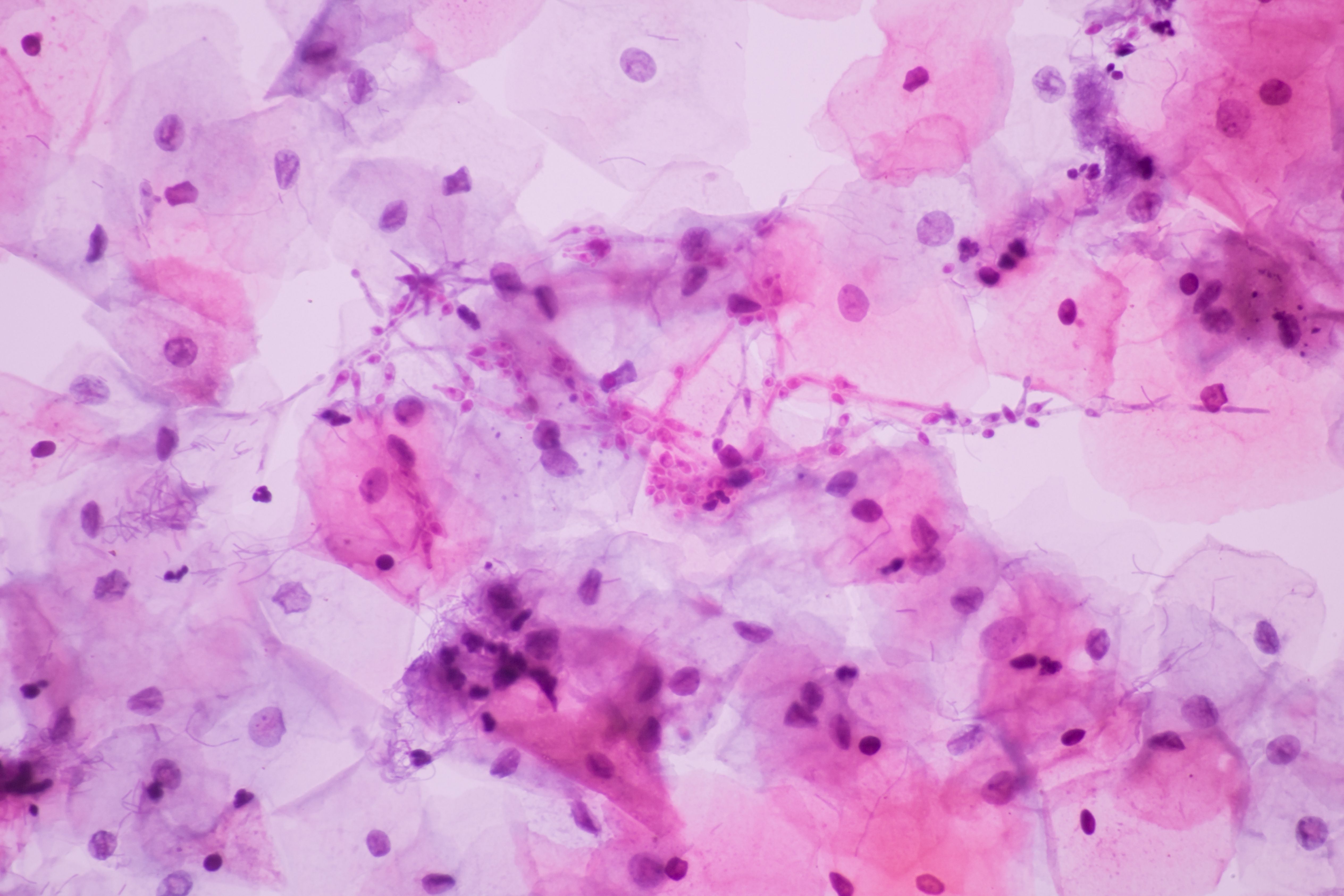
Latest Videos
CME Content
More News

In a recent study, nanostructured lipid carriers loaded with hypericin and dispersed in hydrogels were effective at managing candida albicans.

In a recent study, certain sexually transmitted infections were more common among patients positive for bacterial vaginosis.

In part 2 of this review, more vulvovaginal diseases are examined.

In part 1 of this review, red flags for severe skin disease are discussed.
In a recent study, no severe adverse events were reported in women with vulvovaginal atrophy who were treated with a vaginal tamoxifen capsule.
A multi-targeted rapid sample processing and testing system has shown efficacy for diagnosing vulvovaginal candidiasis by detecting the presence of Candida species in women.

At the 2023 ACOG Annual Clinical & Scientific Meeting, a look at how AI and immunofluorescence scanning microscopy can help in detecting vaginitis and increase the health of the vaginal microbiome.

Three months ago, a healthy 2-year-old girl presented with a mildly pruritic rash with erythematous plaques, some silvery white, in the vulvovaginal area. She had no vaginal discharge or other symptoms. The rash is now more widespread, and new lesions have recently appeared on her lower back and thighs. What's the diagnosis?

The Xpert Xpress Multiplex Vaginal Panel test (Cephid) has shown high agreement for organisms causing vaginitis and vaginosis.

Becton, Dickinson and Company has announced its BD Vaginal Panel received 510(k) clearance from the FDA.

A new study suggests that ospemifene can reduce harmful bacteria and significantly contribute to vaginal health in postmenopausal women.

After observing an increase in the rate of syphilis cases, the Cleveland Clinic Ob/Gyn & Women’s Health Institute has partnered with the Center for Pediatric Infectious Diseases to evaluate the effectiveness of current testing strategies.
New research suggests that adding probiotics to established VVC treatment options may be a path to increased cure rates.

Michael L. Krychman, MD, and Jack D. Sobel, MD, discuss the importance of awareness and education about RVVC, particularly given the impact of symptoms on patients’ psychosocial and sexual behavior.

Michael L. Krychman, MD, and Jack D. Sobel, MD, discuss the practical challenges of access to newer, FDA-approved medications for RVVC and how the third-party reimbursement landscape may take shape in coming years.

Experts explore the availability and cost as well as other unanswered questions regarding emerging agents for the treatment of RVVC.

Michael L. Krychman, MD, and Jack D. Sobel, MD, review the mechanisms of ibrexafungerp and how it might fit in the treatment spectrum for RVVC.

Michael L. Krychman, MD, and Jack D. Sobel, MD, review the clinical implications of the recent approval of oteseconazole, which has been shown to be efficacious and well tolerated in RVVC treatment.

Ibrexafungerp (Brexafemme; Scynexis) is now approved for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis and reduction in the incidence of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis (RVVC).

Thought leaders discuss the history of RVVC treatment, including the use of unapproved topical antifungals and the shortcomings of fluconazole.
Bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy may lead to increased risks for preterm birth, preterm delivery, and spontaneous abortion, according to new research in the Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics.

Daré Bioscience announced yesterday that it has received a grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation of $584,986 to support its efforts related to the development of a vaginal thermosetting gel formulation for the delivery of live biotherapeutics that can be reconstituted at the point of care.

A study published in the journal Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that both Nigella sativa (N. sativa) (black seed and black cumin)-honey vaginal cream and the antifungal medication clotrimazole significantly improve the symptoms of vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC).

A research study examined the role of a medicated feminine wash as an adjunct treatment for candidiasis.
Three months after copper intrauterine device (IUD) insertion, nearly 1/3 of women were diagnosed with vulvovaginal candidiasis, compared to nearly 25% of women who received a hormonal IUD, according to a prospective study published in the journal Cellular and Molecular Biology.











